Product management is one of the critical functions of any business as it is responsible for the overall success of the products or services. The range of activities that require the attention of product managers is wide. This diversity of responsibilities and the many interactions with different teams means that product managers need to possess different types of skills.
The number of decisions that product management is involved in has been increasing in recent years. Product managers work closely with teams inside and outside the organization to build and execute a plan to ensure that the product meets its financial and strategic goals better.
What is product management?
Product management is the business area that manages products at all stages of their life cycle, from development to removal from the market. Product management includes not only physical products, but also services, software, and everything else that companies produce and deliver to the market as a result.
A Product Manager (PM) is the person who identifies the customer needs and the business goals that a product is going to suppress. A PM defines what success will look like for a product and assembles a team to transform the vision into reality.
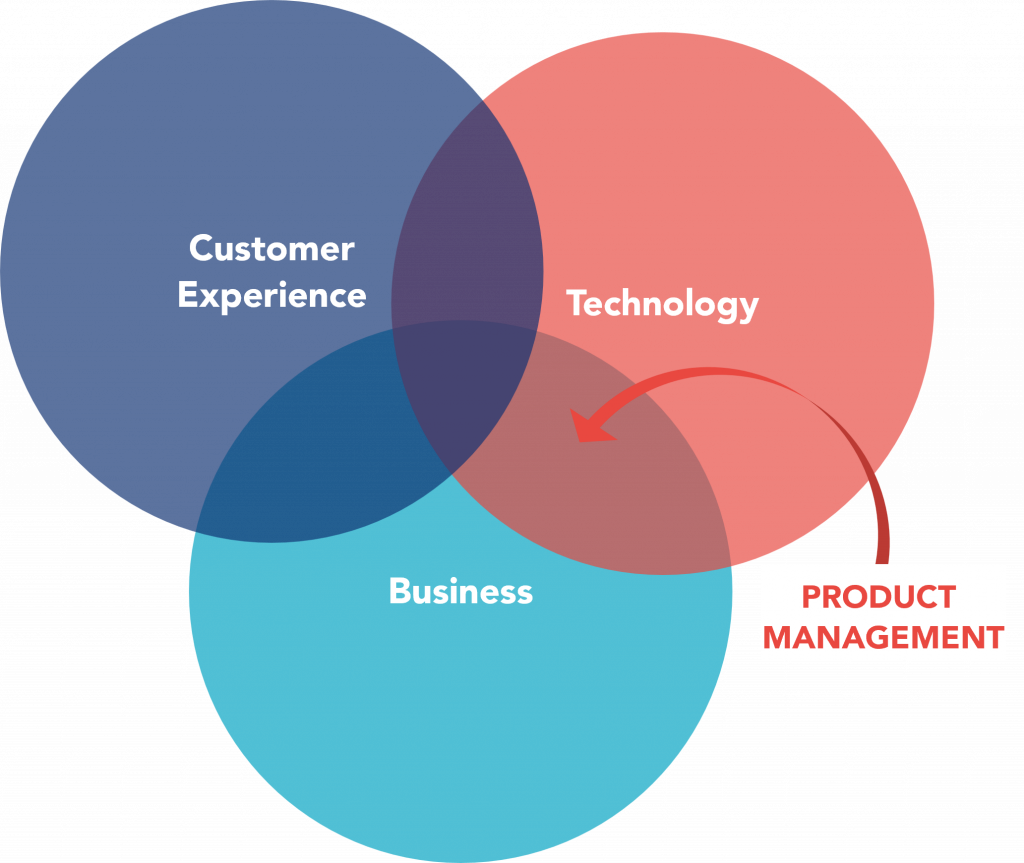
Product management is the crossover between the business, technology, and user experience functions:
Business
The focus of product management is to optimize the product to meet business objectives while maximizing return on investment;
Technology
Product management must have the ability to understand the technology and understand the level of effort involved in building the product;
User Experience
On the other hand, product management is the voice of the user or customer within the business and should know in detail the user’s experience.
What are the benefits of good product management?
Product management helps the company to deliver value to the market and obtain a financial return. The main benefits of having good product management are:
- Delivering the products and services that best meet customer needs;
- Having satisfied customers that generate positive references through word-of-mouth;
- To capture and sustain markets in the long term, through a solid product strategy;
- Increase revenues and business profitability.
What skills does a product manager need?
Given the variety of a product manager’s activities, the skills required to successfully perform their role are also varied:
- Strategic thinking to develop a product vision for the short, medium and long term that is clear and realistic and a plan with desired results;
- Leadership skills to manage multiple teams. The ability to clearly talk to all teams involved and organize the entire product development and market introduction process efficiently;
- Communication skills to effectively communicate critical information to different stakeholders (customers, vendors, development team, management, etc);
- Research and analysis skills to understand the market. Product managers have to follow the market, develop competitive analyses, and be constantly aware of all the current trends to make the best decisions. Market Intelligence can play an important role in providing market insights;
- Technical knowledge to understand the product and technologies and help in the decision-making process;
- Financial skills to analyze costs, and revenues, and define pricing strategies;
- Project management knowledge to manage product development roadmaps and market introductions;
- Continuous improvement skills to test products, analyze data, and identify improvements in a structured way.
What are the responsibilities of a product manager?
The specific responsibilities of a product manager can vary depending on the industry and the size of the company. But these responsibilities are as follows:
- Define the product strategy and vision: Manage the product range and product life cycle and define the vision, positioning, and initiatives to implement for each product;
- Manage stakeholders involved in the product vision: have the ability to communicate with the whole team briefly and clearly;
- Follow the market and develop competitive analysis: be aware of all current trends and have a thorough knowledge of the market to make the best decisions;
- Understand and represent the user’s needs: be close to the customer;
- Launch new products: plan and manage the introduction of products into the markets;
- Define the pricing strategy: define the price list, discount rules, promotional actions and special commercial conditions;
- Train sales and customer service teams: train the teams to sell the new products (points of differentiation, FAQs, Up-sell and Cross-sell suggestions);
- Collaborate in marketing activities: together with the marketing team, develop strategies for product promotion and customer loyalty;
- Ensure continuous product improvement: Test products, analyze data and identify improvements;
- Prioritize resources and product features: have a clear list of development priorities.
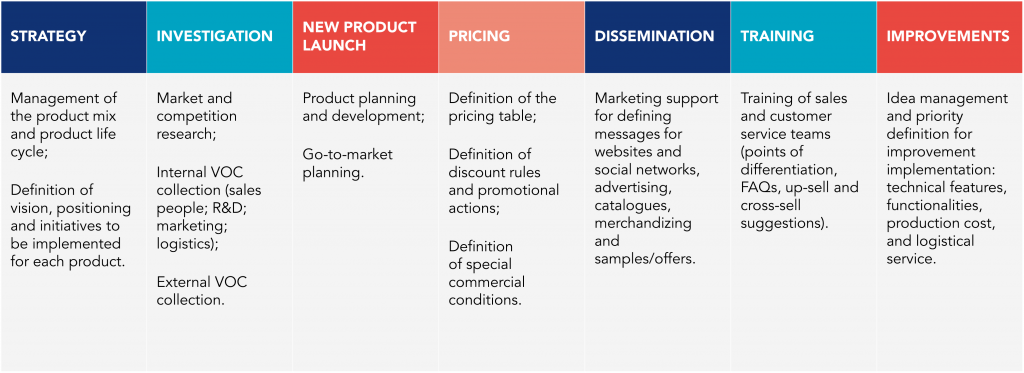
Strategy
Product management plays an important role in defining business strategy because the knowledge it has of products, markets, and competition is essential for decision-making to introduce new products in existing markets or to launch existing products in new markets.
Other strategic activities are the management of the organization’s product range and the management of each product’s life cycle. These activities consist of monitoring the evolution of sales, costs and margins and deciding which products to introduce, invest in, keep, or phase out.
Whenever a decision is made to introduce a new product to the market, it is necessary to define the strategy for what is intended to be achieved before starting to develop the product. This includes defining the product vision, business model, positioning,
pricing model, personas, and segmentation of the target audience.
Investigation
The investigation by the product managers includes three major areas: market and competition, internal teams, and the customer or user.
Market and Competition Investigation
Being aware of the market and competition is essential for any PM. This activity includes activities such as:
- Building lists of direct and indirect competitors;
- Analyze available materials (company website, customer reviews, financial information, …);
- Testing competitors’ products (if possible);
- Document the user experience and identify the strengths and weaknesses of competitors’ products;
- Create a competitive analysis report and share it with R&D, sales, and marketing teams.
Market Intelligence can play a relevant role in this process, as it provides market insights.
Internal Customer Voice Investigation
Collecting and analyzing feedback from internal departments such as marketing, sales, customer support, R&D, and logistics is essential. All these departments may have vital information for improving the product or the buying experience. It is necessary to set standards for collecting the internal voice of the customer in a structured and systematic way.
External Customer Voice Investigation
The PMs must always be close to users and learn the needs and challenges of their customers. To do this, they should participate in the following:
- Calls and meetings with customers;
- Focus groups, polls and surveys;
- Usability tests.
Collection of the voice of the customer, through focus groups or surveys, in a structured way is necessary to design a process. The process should start by defining the purpose of the research and selecting the target audience. Then it is necessary to select the research method and design the data collection forms. After conducting the survey, it is necessary to analyze the responses, compile the data, and share the findings.
New Product Launch
One of the primary responsibilities of the PMs is launching new products. This includes product development and marketing and sales responsibilities to introduce the product to the market.
Active participation of the PMs in product development should happen when designing the product development roadmap, managing the feature backlog, and performing product testing (mock-ups and prototypes).
In planning the market introduction of the products, the PMs must participate in defining the product’s strategic goals, defining the Go-to-Market roadmap, and managing the resources involved.
Pricing
Product managers are also responsible for managing the pricing strategy for the various products, types of customers, and sales and distribution channels.
This responsibility includes activities such as:
- Creating and adjusting the price list;
- Establishing the discount rules;
- Defining promotional actions;
- Establishing special commercial conditions.
Dissemination
Product management must support marketing in defining messages for websites, social media, catalogs, merchandizing, and other means of communicating with potential buyers or influencers of the purchase.
Product managers should complete the StoryBrand of the product segments and products with the marketing team, which serves as the basis for developing marketing and sales content.
Training
Generally, the product manager is the most qualified person to provide product training to the sales and customer service teams.
The teams’ training should include the demonstration of the product and its features and the points of differentiation, FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions), and product suggestions for up-sell and cross-sell.
Using practical demonstrations, role-play exercises, and sales scripts during the training facilitates learning.
Improvements
The PMs must be constantly concerned with improving the value proposition for the customer. To do so, it is necessary to establish an idea management process to improve the technical characteristics and functionalities of the product, but also production costs, logistics service, or others.
Managing in a structured way the customer’s ideas and requests and the feedback from internal teams is essential. A standardized process is essential:
- Registration of ideas and requests;
- Reviewing of ideas and requests and grouping of duplicates;
- Ranking each idea based on consistent criteria, assigning a numerical score;
- Grouping of ideas into categories and sorting by score;
- Transformation of ideas into features and introduction into the product development backlog.
Indicators
Product management indicators help PMs track performance to ensure the company continuously improves and works towards a successful product strategy. The diversity of activities product managers perform means that the performance indicators they track are also different.
The PMs track indicators for sales, costs, margins, quality, service level, customer satisfaction, and retention rates, among others. Indicator tracking and performance analysis should be based on internal and market indicators, such as industry growth, market share, and others.
What is Product Life Cycle?
One of the most relevant activities of product managers is managing the product lifecycle. A product goes through a sequence of stages, from its introduction to the market until it is phased out. This series of stages is called the Product Life Cycle. The activities to be performed by the product manager vary depending on the stage the product is in.
Identifying, recognizing, and understanding a product’s stage is as critical as knowing what each stage requires.
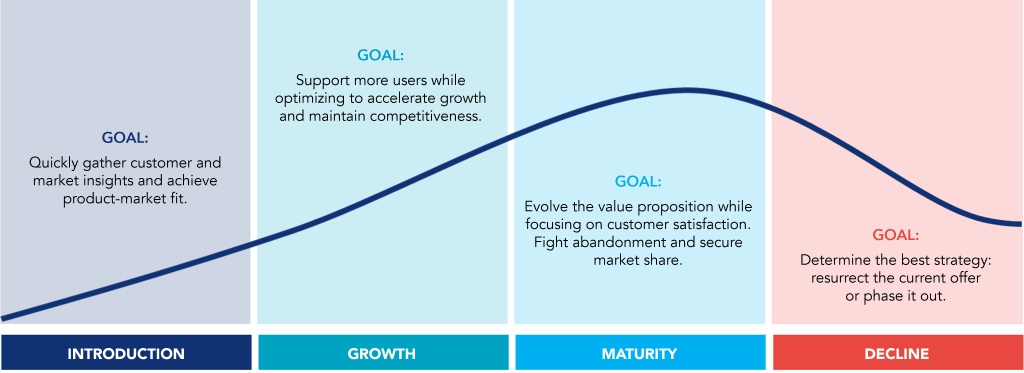
Introduction
The main challenge of this first stage is to generate demand, i.e., to create awareness and communicate the benefits of the product. During this stage, teams must be agile to keep the product viable by emphasizing the different aspects of the value proposition, highlighting relevant features, and eliminating friction points.
Typically, the introduction is the least profitable stage of the life cycle.
In many cases, there is no competition, and it is necessary to define the pricing strategy. There are usually two possible strategies: sell at a higher price to eager early adopters or set a low introductory price to convince as many people as possible.
At this stage the PM should:
- Explain to all stakeholders what the product can actually do and why someone would want to buy and use it;
- When the product starts to gain more users, they should understand who is really using it and what aspects of the product they value most;
- Be an available resource to help the marketing and sales teams.
Growth
This is generally the stage in which the investment in marketing is most significant. The messages that are having an impact and the best channels for customers are identified.
At this stage, it is normal for competition to increase, which may require reducing prices, creating alternative products, or expanding the target market.
In this stage, profit margins increase with economies of scale, and it is necessary to reinvest part of the profit to continue improving the product.
In the growth stage, the PM must:
- Manage the balance so that the products remain competitively priced but without giving away margin unnecessarily;
- Identify who might want to buy the product and what new features or changes are needed to grow the business;
- Analyze the data to discover patterns and trends.
Maturity
At this stage, new customer growth slows, competitors devour market share, and profits decline.
The challenge is to keep as much of the customer base as possible while fighting abandonment.
The role of the PM in this stage is:
- Attempt to reduce costs while continuing to invest in product differentiation;
- Be selective in which features to invest in and how the value proposition evolves. The focus should be on improvements with a high ROI that allow to charge current customers more for new features or open new target markets with a unique offering. The focus on metrics is critical during the maturity stage;
- Understand user behavior and which actions result in continued usage and payments versus those that precede abandonment. It is necessary to analyze the needs for developing nurturing campaigns, targeted promotions, and price changes to keep current customers happy and satisfied for as long as possible.
Decline
The decline can be market-wide or specific to the company’s offering, with competitors outperforming the product in popularity, accessibility, or features.
When the entire market is shrinking, product managers must explore how they can leverage existing technology and branding to continue in a new market.
In the decline stage, the PMs must:
- Understand what scenario is driving the decline to know how to deal with the situation;
- Discover how to get former customers to come back. Identify the profile of former users with the most potential to return and understand which messages impact their return most.
- If the decision is to remove the product from the market, try to make the transition seamless for the remaining customers.
The Importance of Product Management for the Business
Product managers today face complex challenges given the ever-changing demands of customers and the speed of technological change.
Organizations that manage to improve the different areas of product management will stay ahead of the competition and achieve sustained growth. To do so will require:
Improve the information available
Ensure that all of the information needed for decision-making is available and turned into insights (buyers’ needs, technologies, market sizes, and dynamics, etc.);
Improve product management teams
Optimize product management strategy and teams by developing new processes, reorganizing resources, and improving collaboration with the entire company;
Improve product development
Improve product development effectiveness with well-prioritized investment, good backlog management, and reduced product development time.
Improve product introduction to market
Optimize marketing and sales strategies and messages so that they have an impact on new customers and that the market launch of products is successful;
Know and properly manage the Product Life Cycle
Develop and innovate the product or service throughout its life cycle while maintaining financial growth.
Proper product management allows the company to deliver customer value and achieve a financial return.
See more on Sales & Marketing
Find out more about improving this business area
