Using content production and sharing in your marketing strategy is an opportunity to create a more personal contact with potential and current customers.
Nowadays, people have access to a lot of information, which allows them to choose the content they want to consume. At the same time, companies have the necessary knowledge to create content that is fully aligned and focused on what the target audience wants.
The main focus in producing good content should be to provide value to those who consume it, such as clarifying a question, helping to solve a problem, or educating on a topic. The sale is something that appears naturally, as a consequence of this process. Helping potential customers when in need makes them see your brand as an authority in their field, and they start to make a connection. People are more likely to buy from brands they know and like, than from unknown brands.
In other words, content marketing is currently one of the most important strategies, not only for attracting and nurturing potential customers but also for building customer loyalty.
What is content marketing?
Content Marketing is a marketing strategy focused on creating and sharing valuable, relevant and consistent content to attract and retain a target audience.
It is one of the core pillars of inbound marketing and also one of the fastest-growing strategies in recent years. As mentioned, it consists of investing in content to educate and help the target audience, creating a relationship of trust and authority that leads the customer to the moment of purchase. After the first purchase, this strategy plays an important role in building customer loyalty.
The content must contain important information for the potential customer and thus create value for those who consume it, always having a direct connection with the business, the product or service.
What are the advantages of content marketing?
Content marketing brings several benefits to organizations that implement it effectively. Some of the advantages of using a good content marketing strategy are:
- Improve SEO and increase site traffic: Producing relevant content is essential for SEO. It is one of the best ways to get your site to the top of Google searches, where it can be found by your target audience.
- Increase brand awareness and attachment: Content production helps more people get to know the brand and its products and services, and to increase interactions. People are more likely to buy brands that are familiar to them and with which they have a connection. On the other hand, by sharing relevant content, brand ambassadors that promote the brand are developed.
- Teach the market: Content production allows you to answer potential customers’ questions and teach them about everything they need to know to make the best decision at the time of purchase in order to solve their problem.
- Increase the number of leads: Content production allows you to drive more traffic to your site and convert those visitors into leads. Offering relevant content allows you to ask potential customers for contact in a natural and effective way.
- Reduce the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): A content marketing strategy generally brings down the CAC; that is, compared to other acquisition strategies, it has a generally lower cost.
- Increase customer loyalty: Using content marketing in post-sales helps to strengthen the relationship with existing customers. These contents can be related to the use of the product or service itself so that the customer can get the most out of the purchase made.
- Generate more and better sales: For all the benefits mentioned above, it is easy to understand that content marketing also contributes to increased sales. Content production guides leads through the entire buying process and prepares them for decision-making.
Types of content
One of the foundations of content marketing is to generate relevant content that interests the target audience, promoting interactions and connection with the brand. If the goal is to use content to optimize the sales process, you need to think about content that helps potential customers through the various stages of the funnel so that they can evolve between the stages.
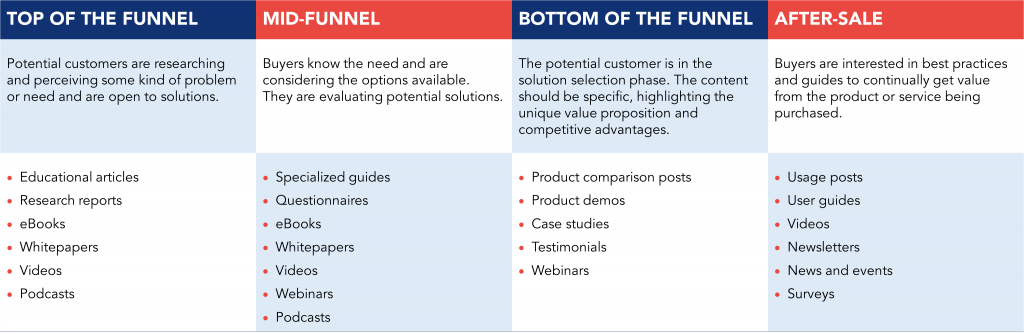
Top funnel content
The top of the funnel is the initial stage, in which the customer is still learning and discovering. At this stage the public is not yet looking for solutions to any specific problem. Many times, the potential customer doesn’t even recognize that there is a problem to solve and is just researching information on a given topic.
The goal of the top of the funnel is to attract attention to discover the problem and lead the audience into the buying process.
At this early stage, the content should have no barriers to consumption. It is necessary to develop interesting content that will make the potential customer return to the site and become familiar with the brand. It is essential to bring the visitor into the funnel.
Some examples of content that can be produced for the top of the funnel are blog posts, web pages, videos, podcasts, and informative ebooks.
Mid-Funnel content
The middle of the funnel is the stage where recognition and consideration happens. People have already discovered that they have a need and are looking for ways to solve their problems. It is already acceptable to create a barrier to content consumption, such as a form, that will turn an interested party into a lead.
Ebooks and whitepapers are crucial in the middle of the funnel, as they are a great way to get qualified leads. Blog posts, surveys, and videos are also a good option, but with a focus on solutions rather than informing. Webinars can help clarify questions from leads and help companies position themselves as experts in their field, and are therefore relevant at this stage of the process.
Bottom funnel content
At this stage, people are already considering buying the product or service and are looking for information that will help them make the decision about which solution and which provider. The more information and contact with the company potential customers have, the more confidence they will have in buying from a given company.
Bottom of funnel materials should be very focused on the company and the product or service.
Customer testimonials and case studies are good examples of content for this stage, as they show how the company has already solved similar problems, which creates confidence for the potential customer.
Webinars and demonstrations focused on the use of the products, are good options, because besides eliminating any doubt about the value of the solution, they can lead the likely customer directly to the purchase.
Content for after-sales
The after-sales is the stage focused on the retention and loyalty of customers who have already made at least one purchase. The investment in content marketing should not end when the sale is made. Acquiring a new customer is much more expensive than bringing back someone who has already bought.
Content marketing can help in creating a relationship with the customer. The company already has information about the customer. It can offer personalized content that helps the customer get more out of the purchased product to solve the problem faster.
Blog posts, infographics, videos explaining how to use the product or service can all be great options. Any content format that generates value for those who have already purchased the solution and keeps them satisfied with their purchase is a good option.
Content production
Creating quality content requires investment of time, dedication, and work. To develop quality content it is necessary, on the one hand, to know the product, the business and the market well, and on the other hand, to know the best practices of content production.
The following describes some factors that must be taken into consideration when producing content. Knowing that the first step is always to know your target audience and their problems and needs.
Selection of key words and expressions
Keywords are terms or phrases that people use when searching on the internet. Keywords are essential for SEO (Search Engine Optimization), that is, for optimizing content to appear at the top of search engines.
The use of keywords in the content is important for Google to correctly index the page for the desired terms, but the same word should not be repeated consecutively. Semantics are essential. The semantic field of the term should be explored, with its variations, synonyms, and relationships with other words.
It is necessary to find out which keywords are relevant to the business and invest in producing content on that topic. There are several tools that can help in this process.
However, it is important to never forget that content is primarily directed to a target audience and not to a search engine.
Content size and format
The size and format of the ideal content may vary from site to site. After all, the most important thing is to deliver value to the reader.
A broad keyword, with a lot of competition and search volume, requires a very complete content. A post about something very specific, with less research and competition, can be shorter and more direct.
The important thing is to avoid unnecessarily long and complicated texts or too short and lacking information.
A good length is between 2,000 and 3,000 words, enough to answer the persona’s questions and long enough to benefit Google, which tends to favor more complete texts.
It is important to vary the format to keep the audience interested. You can offer articles, questionnaires, infographics, videos, podcasts and experiment with new formats to test what has the most impact on the intended audience.
Scannability
Scannability is the ability of a text to provide dynamic reading through features such as intertitles, lists, boldface, and images. By being different, these features draw the reader’s attention and inform that those points are important and need to be read.
Scannability makes it possible to improve the reading experience, hook the user, and transmit information to Google.
For example, by creating intertitles, both the reader and the robot can better understand the hierarchy of the text.
It is also important not to forget the importance of using short sentences and paragraphs. Large blocks of text impair the understanding of the message concerning where a line of thought begins and ends.
Revision
A flawed piece of content can wipe out all the authority you have fought to build. All the content produced must be reviewed, not only to find errors but to see if it fits the standards presented above.
Ideally, the revision should not be done by the person who developed the content.
The brand’s A3 as a basis for content development
To grow businesses, you have to simplify the message you deliver. This is made possible by using the A3 from the brand’s history. This methodology serves as the basis for all the content to be produced, simplifying the message and making it easier to talk about the brand. In this way customers will be more attracted to the products or services that the company offers.
The goal is to discover the customers’ story and put the company right at its center. A story is the only thing that can hold a human being’s attention for hours.
Almost all stories are built this way: A CHARACTER who wants something encounters a PROBLEM before being able to reach it. At the peak of despair, a GUIDE enters their life, gives them a PLAN, and CALLS THEM TO ACTION. Action helps to prevent FAILURE and to end with SUCCESS.
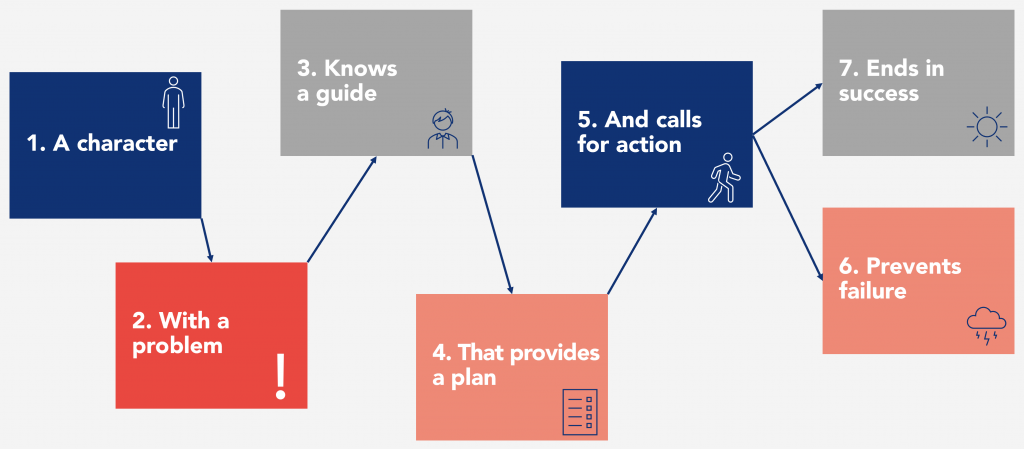
1. Character: The customer is the hero
Many companies have not yet realized the paradigm shift they have to make when telling the brand story: the customer is the story’s hero, not the brand.
By positioning the customer as the hero and the company as the guide, the company will be recognized as a trusted resource to help the customer overcome challenges. It’s a small but powerful change that honors the customer journey and positions the company as a leader, bringing wisdom, products, and services that the public needs to thrive.
Once you identify who the customer is, you need to ask what they want as far as the brand is concerned. The catalyst of any story is the hero wanting something. The rest of the story is a journey about finding out if the heroes got what they wanted.
2. Problem: companies sell solutions for external problems, but customers buy for internal problems
Usually, a story begins with a character who lives in peace. Suddenly, stability is interrupted: a bomb goes off, someone is kidnapped, or disaster strikes. The heroes then set out on a journey to return to the peaceful life they once had.
Customers are attracted to the company because they want to solve a problem that has disrupted their life. By talking about the problems that customers face, you deepen interest in everything the company offers.
There are three levels of problems that a customer encounters, just like heroes, external, internal, and philosophical problems.
- External problems: physical and tangible problem that the hero must overcome
- Internal problem: frustration the hero feels because of the external problem
- Philosophical problem: a problem greater than the story itself
Specific examples for an electric car brand:
- External problem: needing a car
- Internal problem: wanting to be an early adopter of new technologies
- Philosophical problem: my choice of car should help the environment
Almost all companies try to sell solutions to external problems, but customers are much more motivated to solve their internal frustrations.
3. Guide: customers are not looking for another hero, they are looking for a guide
If the heroes of a story could solve their own problems, they would never get into trouble. That is why storytellers over the centuries have created another character to help the hero win: the guide.
Most human beings look for guides to help them overcome their problems. Every human being wakes up every morning and sees the world through the lens of a protagonist. When a brand comes along and positions itself as the hero, customers stay away and hear about how great the business is and start to question whether the company is competing with them for scarce resources.
For a company to position itself as a guide, it has to demonstrate empathy on the one hand, and authority on the other. Empathy will show the customer that you understand the difficulties they are experiencing. Authority will prove that one has the necessary skills to help you. There are many ways to demonstrate authority: through testimonials from other customers, years of experience, awards or certifications, or any other means that proves the company is capable of helping the customer.
4. Plan: customers trust a guide who has a plan
At this point you have identified what the customer wants, defined three levels of problems, and positioned the company as a guide. But customers still won’t make a purchase because you haven’t outlined a simple plan of action that they can follow. What customers are looking for, is a clear path that removes any confusion that may exist about how to buy.
There are two types of plans: the process plan and the agreement plan. Each of these plans gives confidence and offers customers a clear path to stability, greatly increasing the likelihood that they will make a purchase.
A process plan can describe the steps a customer needs to take to buy the product, or the steps to use the product after buying it, or a mixture of both.
If the process plans are to lessen the confusion, the agreement plans are to lessen the fears. This is a list of agreements you make with customers to help them overcome their fear of doing business. The best way to come up with an agreement plan is to list all the customer’s fears regarding the product or service, and then counter that list with agreements that will address the fears or objections.
5. Call to Action: customers only take action if challenged
In the stories, the characters do not take action on their own initiative. They only take action after being challenged by an external factor. This principle is valid in stories because it is also valid in life.
A call to action involves communicating a clear and direct step that customers can take to overcome challenges and return to a peaceful life.
There can be two types of calls to action: a direct call to action, asking the customer for a purchase or to schedule a meeting; or a transitional call to action for customers who are not yet ready to buy, i.e. something that promotes the relationship with the company.
Once you start using both types of calls to action in your messages, customers will understand exactly what we want them to do and decide whether to let the company play a role in their story.
6. Avoiding failure: everyone wants to avoid a tragic ending
The stories live and die on a single question: what is at stake? If nothing can be won or lost, no one cares. Similarly, if there is nothing at stake, if there is no obvious benefit in buying a product, the customer may decide not to proceed with the purchase.
It is necessary to show people the cost of not doing business. Brands that help customers avoid some kind of negativity in life, and that let customers figure out what that negativity is, engage customers for the same reason that good stories captivate an audience: they define what’s at stake.
7. Ending in success: telling people how the brand can change their lives
Customers need to be told how good their life can be if they buy the company’s products or services. Everyone wants to be taken somewhere. If you don’t tell people where they can go, they will buy from the other brand.
Probably the most important element of the messaging strategy is: offering a vision of how good a customer’s life can be, if they buy the company’s products or services.
By putting these seven elements together, we come up with a tool to simplify the process of writing the story. This tool will allow you to create a clear message, save time, and motivate the creation of marketing material that works.

This A3 is usually done at different levels. The first level is the brand’s general A3. Then A3s are created for each business segment of the company. And finally, for each product within the segments.
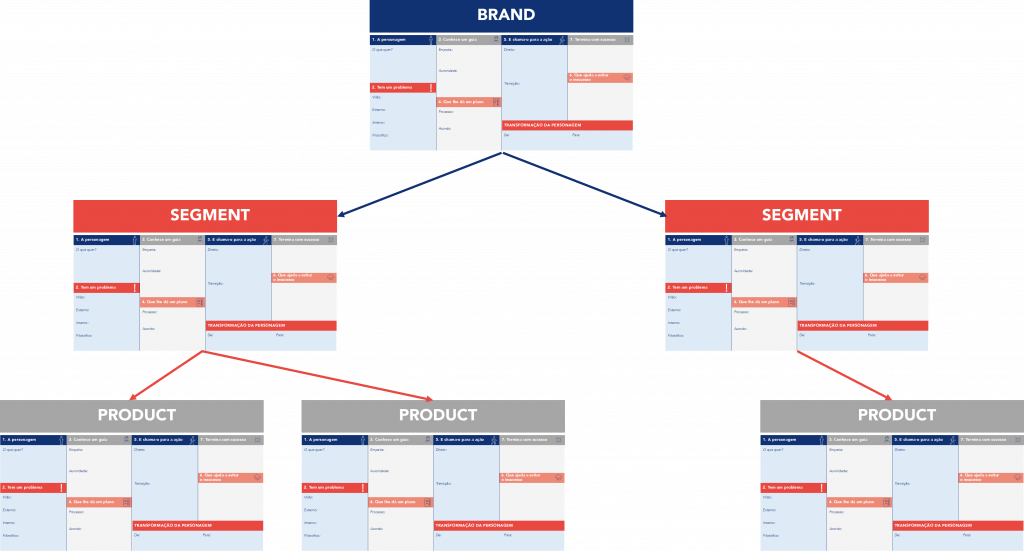
The A3 with the story is a powerful resource that helps organize and simplify the message and use it repeatedly and can and should be used to grow the business.
Once the company has the A3s of the brand history, segments, and eventually products as well, producing content becomes a simpler process.
Definition of best practices for content production
Marketing content comes in many different formats (articles, emails, website pages, landing pages, videos, …). It is important to develop a set of best practices to guide those who are developing them.

By having good A3s of the brand and product history and good standards for the different formats, successful content is more likely to be produced. In other words, there is not exactly a secret, but there are good practices that can help to be more efficient and effective.
Content: a core element of any growth strategy
Once targeting is well-defined, companies are ready to start studying the needs and problems of the target audience in order to produce relevant content.
Content marketing answers target audience questions, helps build trust and develop brand relationships, improves conversions, generates leads, and contributes to customer loyalty. Today, all customers expect consistent, high-quality content from their favorite brands.
See more on Sales & Marketing
Find out more about improving this business area
