In the current innovation landscape and heightened competition, lean product development is central to organizations’ strategies. In this context, the product design phase is crucial, establishing not only the functionality and aesthetics of the product but also its market acceptance and ability to stand out against the competition. The success of this phase isn’t just dependent on the team’s inspiration or creativity; it requires a robust methodology to systematically and efficiently guide the design process. Lean Product Design (LPD) stands out as an approach that accelerates the development process and works on minimizing risks and maximizing the chances of success.
Introduction to Lean Product Design
Lean Product Design is more than just a product development approach; it’s a philosophy that aims to maximize customer value while minimizing waste and optimizing efficiency at every stage.
This methodology focuses on listening to the voice of the customer, influencing each phase of the design process. Companies can tailor their products to meet market needs by translating customer insights into tangible requirements. Converting customer requirements into product requirements ensures that development meets expectations. Additionally, proactively identifying potential flaws makes it possible to anticipate and correct issues, resulting in performance, quality, and product reliability improvement, thereby promoting sustainable operational efficiency.
Key Principles of Lean Product Design
As previously mentioned, Lean Product Design is an approach that optimizes product development by eliminating waste and focusing on delivering value to the customer. Here are the fundamental principles guiding LPD:
- Understanding Customer Value: This involves identifying and prioritizing the features and functionalities that are genuinely significant to users. By aligning product design with what matters to customers, teams can avoid creating unnecessary features and focus their efforts on what truly adds value.
- Eliminating Waste: This includes identifying and removing activities and resources that do not directly contribute to value creation. By reducing waste, teams can speed up product development, cut costs, improve the overall efficiency of the process, and reduce Time-to-Market.
- Working in Cross-Functional Teams: Working with cross-functional teams ensures a holistic approach to product development, integrating diverse perspectives to achieve innovative and efficient outcomes.
- Promoting Iterative Development: Teams are encouraged to iterate, build prototypes, obtain customer feedback, and continuously adjust the design. This iterative cycle allows agile adaptation to customer needs and reduces the risk of developing products that do not meet expectations.
- Incorporating Quality from the Start: The quality design principle emphasizes the importance of integrating quality practices from the early stages of the process. By prioritizing quality from the beginning, the likelihood of defects is reduced, ensuring customer satisfaction and avoiding rework and other future costs caused by non-quality.
By grasping and implementing these core principles, development teams can develop highly valuable products for the market.
Benefits of Lean Product Design
Lean Product Design offers a range of benefits for organizations. Let’s explore the benefits of adopting and implementing LPD:
- Agile Response to Market Changes: By adopting an iterative and customer-centered approach, teams can quickly adjust their products to meet constantly evolving needs.
- Significant Reduction of Waste and Costs: By identifying and eliminating activities and processes that do not add value to the final product, organizations can optimize resources, reduce operational costs, and increase overall efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement of Product Quality: By receiving constant feedback from users, teams can enhance functionality, usability, and reliability, resulting in high-quality products that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Team Motivation: By improving collaboration among teams, minimizing rework resulting from late problem detection, and designing higher quality products, teams experience a more significant sense of accomplishment, contributing to an increase in motivation.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction and Brand Loyalty: Satisfied customers are more likely to become brand advocates and remain loyal to products that continue to evolve alongside their expectations.
- Reduction in Time-to-Market: By eliminating redundancies, simplifying processes, and adopting an agile approach, organizations can bring innovative products to market more quickly (reduction of Time-to-Market), capitalizing on opportunities and gaining a competitive edge.
By adopting LPD, companies create innovative products and position themselves to thrive in a dynamic and competitive business environment.
The Lean Product Design Process
Lean Product Design is a process organized into several stages, where the Voice of the Customer, the Customer and Product Requirements, and the FMEA methodology converge to create truly exceptional products.
Voice of the Customer
The Voice of the Customer (VOC) is an essential tool for understanding consumers’ needs, requirements, and expectations.
VOC refers to all methods used to gather valuable market insights. It’s the way companies tune in to consumer feedback, creating a bridge between customer expectations and business strategies.
The Voice of the Customer provides input guiding decisions across all areas of the organization, from marketing to product planning and business strategies, minimizing costs and rework caused by poor choices.
The Voice of the Customer can be collected through various methods, including:
- Verbal or written statements (interviews, direct feedback, and comment analysis);
- Surveys (questionnaires and online feedback);
- Observation of purchasing behaviors;
- Study of customers’ habits and practices;
- Analysis of body language.
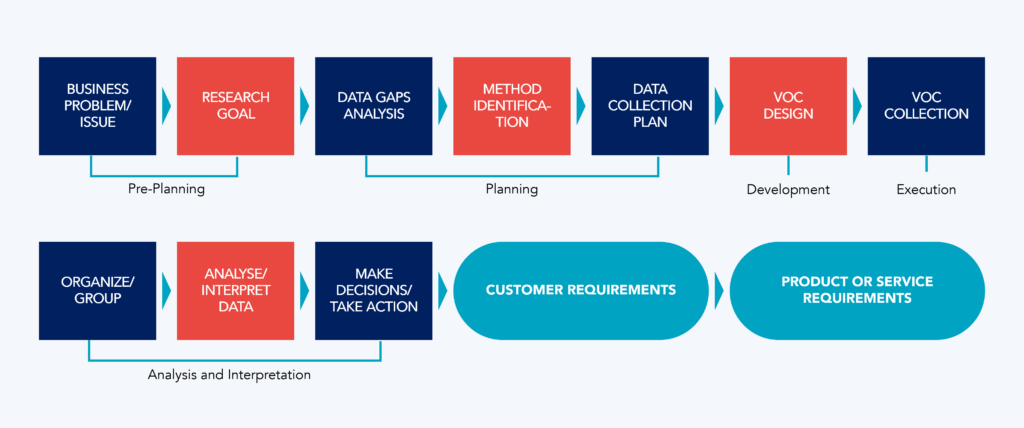
In summary, the Voice of the Customer is a strategic approach that guides the entire LPD process, and the strategies for data collection can vary depending on the type of research desired.
Customer Requirements
A deep understanding of Customer Requirements is a crucial step in the LPD process. This stage involves transforming the Voice of the Customer into clearly identified and measurable requirements.
The main stages to defining customer requirements are:
- Understanding Customer Needs and Defining Use Cases: Analyzing the voice of the customer to understand expectations and motivations and creating specific examples that describe the customers’ needs in a clear and detailed manner.
- Discovering and Analyzing the Competition: Understanding competitors to define project priorities and identify gaps in the market.
- Assigning Importance: Identifying Must-Have and Desirable requirements to prioritize key elements in product development.
- Categorizing Customer Requirements: Identifying all categories representing different dimensions of interests.
- Identiying Customer Requirement Decision Variables and Assigning Values: Define the variables related to customer requirements and, for each decision variable, clarify the target value, the acceptable value, and the current value.
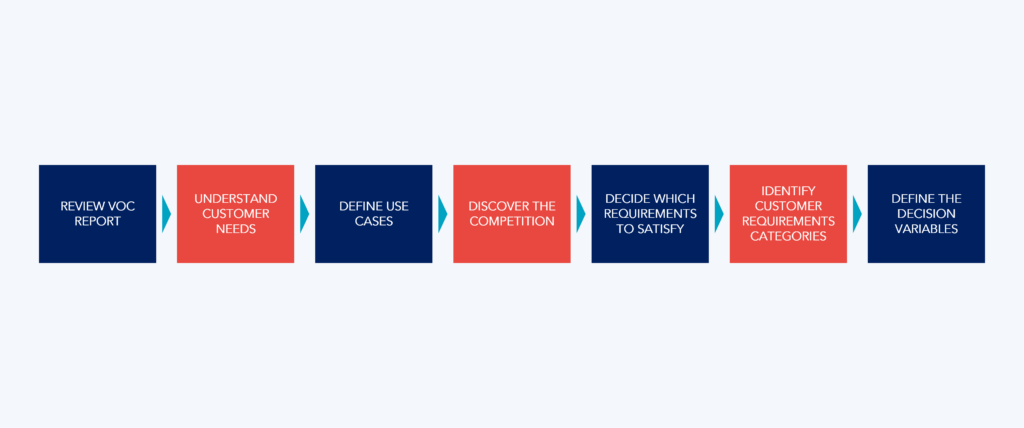
These steps support the necessary foundation for LPD, ensuring that the developed products satisfy and exceed customer expectations.
Product Requirements
Product Requirements play a crucial role in Lean Product Design, providing the basis for informed decision-making from the initial stage of the product development process.
In this phase, it is vital to have a multifunctional and collaborative team encompassing various areas such as marketing, quality, design, and engineering. The lack of early joint decisions can lead to poor product definition, frequent development changes, and launch delays. A collaborative team ensures a more focused project direction, better product conception, and effective planning for a quicker market launch.
The process of transforming customer requirements into product requirements is based on four phases:
- Quality Function Deployment (QFD): QFD is a technique that translates customer needs into specific product features. It ensures that the product requirements are directly aligned with consumer expectations.
- Establishing Baseline: Understanding the current product design and associated costs provides a solid foundation for defining future requirements. This helps to identify areas for improvement and innovation opportunities.
- Product Concept Process: Creating product concepts involves creatively exploring solutions that meet the defined requirements. At the end of this phase, usually only 2 product concepts remain.
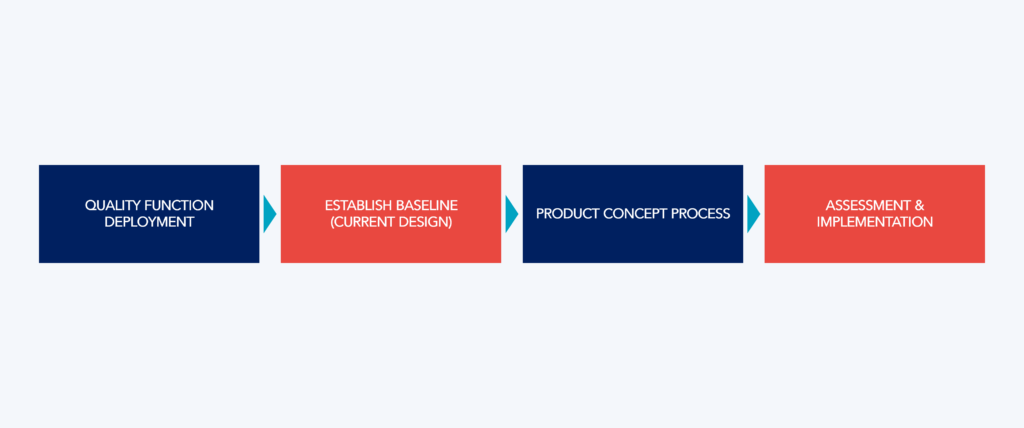
Establishing Product Requirements correctly is crucial to avoid future problems. A collaborative approach supported by a well-structured methodology establishes a solid foundation for efficient LPD, ensuring an effective delivery aligned with customer expectations.
Product FMEA
Product Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach that is pivotal in Lean Product Design, enabling proactive risk management throughout the product lifecycle.
The product FMEA process can be summarized in the following steps:
- Identification of Potential Failures: The first step involves systematically identifying ways the product might fail. This includes a detailed analysis of critical design functions and anticipating possible failure modes.
- Estimation of Risk Associated with Specific Causes: Once the failure modes are identified, the risk associated with specific causes for each failure mode is assessed. This involves analyzing Occurrence (probability of happening), Severity (difficulty if it does happen), and Detection (likelihood of being identified) to estimate the Risk Priority.
- Definition of Actions to Reduce Risk: With a clear and comprehensive understanding of the risk associated with each cause of failure, actions are defined to reduce the risk. This guides the design team in implementing preventive measures.
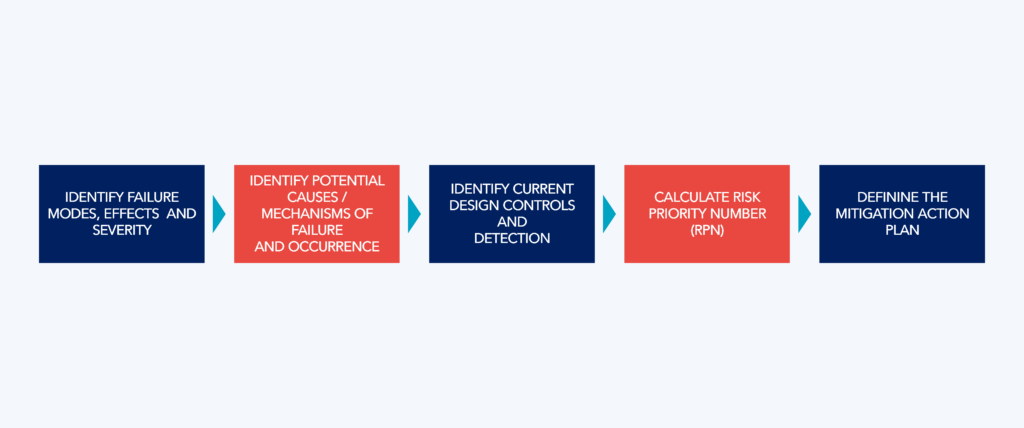
Product FMEA is an indispensable tool in LPD, offering a structured approach to identify, evaluate, and mitigate potential risks. By adopting this methodology, teams can strengthen the product’s quality, reliability, and safety, ensuring more efficient and customer-oriented development.
Conclusion
By understanding the fundamental principles of Lean Product Design, such as focusing on customer value, eliminating waste, promoting iterative development, working in cross-functional teams, and incorporating quality from the start, we realize that these guidelines drive the efficient creation of innovative products. The consistent application of these principles allows development teams to create products that satisfy and exceed market expectations. Moreover, by adopting LPD, organizations innovate and position themselves to succeed in a dynamic and highly competitive landscape, placing customer satisfaction as a guiding beacon for ongoing success.
Still have questions about Lean Product Design?
What are the Customer’s requirements?
Customer Requirements refer to customers’ needs, expectations, and specifications regarding a product or service. These requirements are obtained by understanding the Voice of the Customer and actively listening to customers’ opinions, requests, and feedback. Customer requirements are the foundation for developing a product that meets their expectations and fulfills their needs.
What are Product Requirements?
Product Requirements are the features, functionalities, and technical specifications a product must have to meet customer requirements. In other words, they are the practical and tangible translations of customer requirements to guide the product design and development process. Transforming customer requirements into product requirements is a fundamental step to ensure that the final product is aligned with customer expectations on performance and ease of use.
See more on Lean Product Development
Find out more about improving this business area
