Products are one of the most relevant elements for a company’s success. Creating a successful product range is becoming more and more challenging as the supply has grown due to the ease of access to a global market with increasingly demanding and less loyal customers.
For the customer to recognize the value of the products, it is necessary to have a good marketing and sales strategy, and product positioning is the basis for defining this strategy. Product positioning is a strategic exercise that analyzes and defines how the product fits into the market and why it is a better solution than existing alternatives.
The best products are characterized by a distinctive positioning and a value proposition that focuses on the specific needs of the target customer. It is necessary to identify the market opportunities, i.e., the segments with unmet needs, and then understand what type of product can meet those needs.
What is product positioning?
Product positioning refers to strategies that allow companies to understand how their products fit into the marketplace to highlight their benefits over the competition and create a positive image of them in customers’ minds.
Product positioning involves identifying the needs and wants of the target audience and then developing a clear and compelling message that meets those needs. The company must communicate this positioning consistently through branding, packaging, advertising, promotions, and other marketing activities.
Product positioning uses various types of analysis to understand how the value proposition meets the market’s needs and how it can stand out from the competition.
How important is product positioning?
Product positioning involves identifying the main features and benefits of the product for the target audience so that the company can communicate these aspects clearly and effectively to the market.
By positioning the product correctly, the company can attract the right audience, increase customer demand and perceived value, and improve customer loyalty. On the other hand, if the company does not position the product correctly, the product can be seen as irrelevant, leading to decreased perceived value and lost sales.
Product positioning is crucial to a company’s success and must be carefully analyzed to allow marketing and sales to do their job better. It allows you to define strategies to improve the product’s fit to the market, identify differentiating factors against the competition, and define marketing and sales strategies according to a product’s competitive advantages, translating into business growth.
In brief, some of the main benefits of product positioning are:
Product differentiation in the market
By uniquely positioning the product, it stands out in the marketplace, which can attract customers’ attention and increase brand visibility. In other words, it allows you to differentiate yourself from your competitors by highlighting your benefits and unique features.
Sales increase
If the product is positioned effectively, this can lead to increased sales. When potential customers perceive that the product meets their needs, they are more likely to buy it.
Customer loyalty
Product positioning can also help create a loyal customer base that identifies with the unique values and benefits the product offers. This can lead to increased customer retention and brand loyalty.
Improved brand reputation
Effective product positioning can help improve the brand image by creating a positive reputation in customers’ minds. This can lead to increased trust in the brand and, in turn, increased sales and long-term success.
How to position the product? Types of analyses
Several methodologies help companies do product positioning analysis. Three of these methodologies are highlighted here: Product-market fit analysis, value curves, and value vs. price matrix.
Product-market fit analysis
Product-market fit (PMF) analysis is the process that evaluates whether a product or service meets the needs and requirements of a particular target market. It involves assessing whether the product solves a significant problem or satisfies a significant need of the target market.
PMF analysis typically involves collecting data from potential customers and analyzing it to determine whether there is a strong need for the product and whether customers are willing to pay for it. The analysis may involve surveys, focus groups, interviews, and other ways of collecting the Voice of the Customer.
Once the data is collected, it is analyzed to identify patterns and trends and determine if the product has a good market fit. This analysis can help product managers and business leaders decide about investing in the product, how to improve it to meet customer needs, and how to position it better in the market.
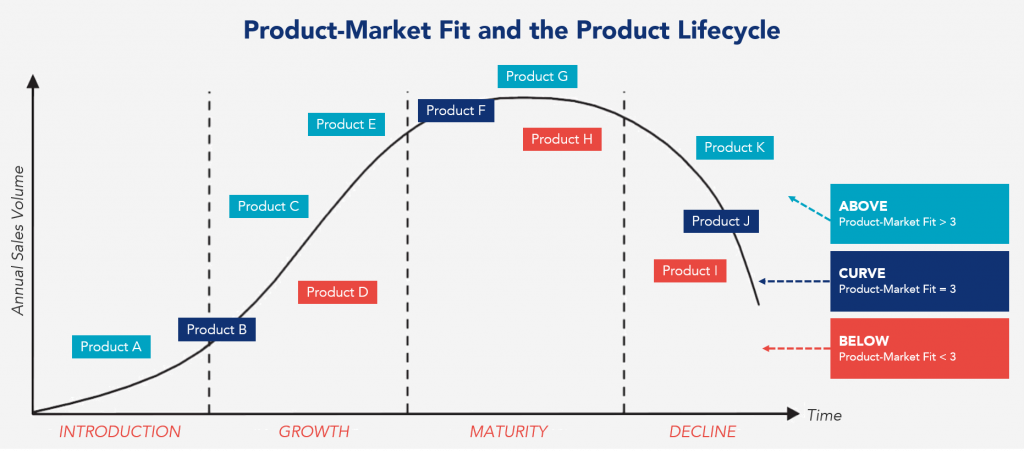
Achieving product-market fit is considered a critical milestone for new products, as it indicates that the product is meeting a significant need and has the potential to be successful in the long term. However, PMF analyses must be performed at all product lifecycle stages since market needs constantly change.
The main steps in performing a PMF analysis are:
- List the various products (or product segments) to be included in the analysis.
- Define the product-market fit criteria to be used.
- Sort the products according to the various PMF criteria. Whenever possible, use the Voice of the Customer.
- Calculate the final value of the PMF by adding up the scores of the various criteria.
- Position the products on the lifecycle curve.
- Analyze the map with the combination of the PMF and the product lifecycle phases and identify the marketing and sales (or product development) strategies to adopt for each case.
- Define an action plan for implementing the strategy.
Value curves
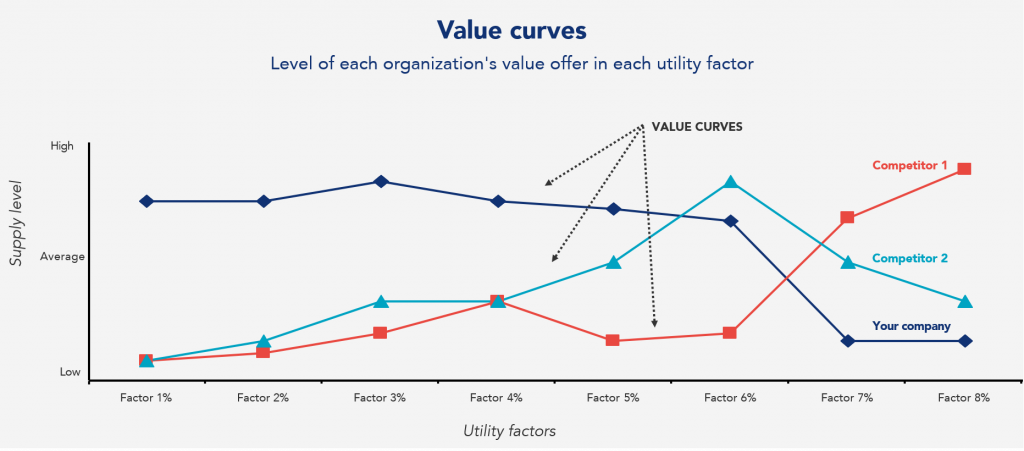
A value curve is a graphical representation of how a product or service delivers value to its customers. It is a way to visualize the various elements of a product or service that contribute to its value proposition. A value curve’s horizontal axis represents a product or service’s various attributes or utility factors. In contrast, the vertical axis represents the degree of value or importance customers attribute to these same factors.
A value curve can be used to compare the value propositions of different products or services in a market and to identify areas where a company’s offering should be optimized to meet customer needs better. Value curves can also identify areas in which a company is investing too many resources and which are less relevant to customers.
The first step in creating value curves is to carry out an analysis to discover the main criteria that customers use to make purchasing decisions.
Usually, the most experienced sales teams know, with some rigor, what is most relevant to customers, but the most correct and reliable methodology is to obtain this information through customer surveys. Questionnaires or interviews should be conducted with customers to determine the most valued utility factors and their weight in the purchase decision.

The purpose of the analysis is to list the most relevant factors for customers when buying, rank them by importance, and evaluate the company and the competition regarding these same factors.
Based on the analysis results, it is possible to build value curves in which it is easy to analyze the most critical factors and their respective weights and information on how customers evaluate the company and its competitors on these same factors .
The main steps for creating the value curves are:
- Perform the analysis of the segment in which you operate, identifying the leading competitors and utility factors, and prepare the data collection.
- Collect the data with customer interviews and surveys;
- Analyze the data collected and draw conclusions about:
- the actual utility factors and their weights.
- the main competing products/solutions on the market.
- the ranking of the product and competitors on each utility factor on a previously defined scale.
- Create the value curves.
- Analyze the value curves and identify the strategy for each product (or product segment).
- Define an action plan for implementing the strategy.
Value vs. Price matrix
Value vs. Price analysis examines the relationship between the price of a product or service and its value proposition as perceived by customers. The products or services’ price and value are the only parameters that genuinely interest the customer, so organizations need to know their interaction.
Value vs. Price analysis helps companies find the balance between the value the product or service offers and the price customers are willing to pay. As such, it becomes an important tool to help companies adjust their pricing strategy and refine their value proposition to meet their customers’ needs and desires better and achieve greater market competitiveness.
Once the value curve information is available, creating the Value vs. Price map becomes quite simple. The total value is calculated by taking the weighted average of the scores assigned to each utility factor (excluding the price factor, which will be represented on the vertical axis).
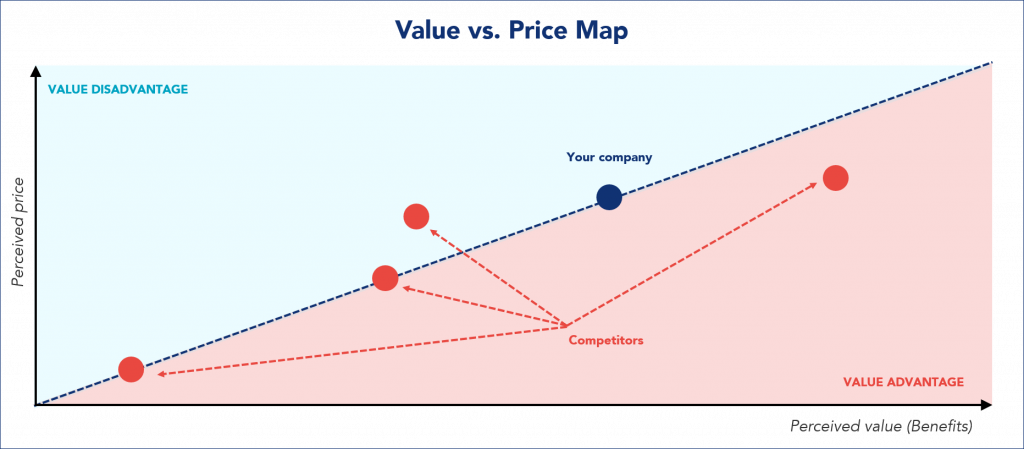
If the market operated under conditions of perfect competition, where the customer would have full knowledge of the market, all products and services would be on the balance line. But what happens, in reality, is that they are often above or below due to the customers’ imperfect knowledge of the market options or other factors. Products above the balance line tend to lose market share, while those below it gain, as customers realize that there are products that give them more value for the same price.
Value vs. Price analysis allows companies to visualize their current competitive position in the market and evaluate the options available: change the price of the product, the value offered, or any combination of the two to some or all customers. For example, a product below the balance line could maintain its value constant and increase its price or maintain its price and reduce its costs, resulting in higher revenues.
Even if using the Voice of the Customer to collect the data needed to create these maps is impossible, organizations should not refrain from carrying out this analysis. In such cases, some map information may be based on opinions, but a rough map is always more helpful for strategic purposes than no map. It can be a suitable means of making important marketing and sales decisions.
After analyzing the Value vs. Price map, it is necessary to define which strategy to adopt for each product or segment and build an action plan for its implementation.
The importance of product positioning for business growth
In light of all the above, it is easy to conclude that product positioning is an essential activity for any business, as it assesses how a product is perceived by customers compared to its competitors and helps define strategies for the company to improve this perception.
Product positioning should be created whenever possible based on the Voice of the Customer and not just based on opinions and perceptions. However, being unable to hear the Voice of the Customer should not be an obstacle to conducting these analyses.
The three analyses described above allow the company:
- To study the competition: understand how the competitors position their products and thus identify opportunities for differentiation.
- To identify the unique benefits of the product: understand the unique benefits that the brand offers and that competitors do not.
- To improve the pricing strategy: understand whether the product is at a value advantage or disadvantage.
- To define and communicate a clear message: The positioning message must be clear and easy to understand. It should highlight the product’s unique benefits and how they meet the needs and wants of the target audience.
Successful product positioning can bring numerous benefits to the business, such as: improving customer perception of product value, creating a strong identity with a cohesive and consistent brand image, and increasing customer loyalty, which translates into increased sales. Simply put, product positioning is an essential strategy for the success and growth of any business.
See more on Sales & Marketing
Find out more about improving this business area
