Providing a great experience to potential buyers dramatically impacts the buying decision. Studies show that the buying experience generally has more influence on the decision than product features or price.
Benchmarking shows that companies that offer great buying experiences grow twice as fast as companies that provide average experiences.
A good shopping experience generates more traffic, higher conversion rates, higher average purchase values, shorter sales cycles, and more positive customer referrals. The result of all this is a faster growth rate.
By providing buyers with a great experience, the result will be to have sales metrics continually improve.
Organizations that use tools to analyze buying journeys to evaluate customer interactions and continuously improve them are one step ahead of the competition.
What is the Buying Experience?
The buying experience is the entire journey in which a potential customer is involved, from first becoming aware of the need or problem to receiving and using the product or service for the first time.
One can say that the customer buying experience results from the interaction between the organization and the customer throughout their relationship. It entails involvement on different levels: rational, emotional, sensory, and physical. In other words, the experience is the cumulative impact of multiple touchpoints over time.
Why map the Customer Buying Experience?
Customer satisfaction should not be analyzed and measured separately. The results can be misleading when the evaluation is done independently at each touchpoint.
Customers may interact multiple times with the company as part of a process or journey, and one should not view these interactions as isolated. Customer Journey Maps allow you to address this problem and see the process as a whole from the customer’s point of view.
What are the benefits of Mapping the Customer Buying Experience?
Mapping the customer experience during their buying journey allows organizations to identify the main improvement opportunities. These are the main benefits of this methodology:
Increase the conversion rate:
A good experience has a big impact on the buying decision.
Increase the value of repeated sales:
Satisfied customers tend to buy again and increase the average ticket.
Increase the customer retention rate:
Satisfied customers become loyal to the brand, decreasing the number of lost customers.
Increase the number of brand promoters:
Customers with good experiences become brand promoters, which attracts new customers.
Decrease the number of brand detractors:
In a highly connected world, it is important to avoid negative experiences.
Reduce the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC):
Word of mouth yields many new customers, allowing for lower investment in paid advertising.
What is a Buying Journey Map?
A buying journey map, or buying experience map, is a diagram that reflects the possible interactions that the customer may have with the company. It maps the customer journey: actions taken, services used, and their sequence.
It analyzes the experience of each customer segment and allows it to evolve from a transactional relationship to a customer-centric relationship.
The analysis of pain points and satisfaction points allows for understanding how each interaction with the company generates or destroys value from the customer’s point of view.
How to Map the Customer Experience?
The customer journey mapping should always be done through the eyes of the customer, and most of the time, it is necessary to gather information from the Voice of the Customer.
The goal is to get a visual sketch of the stages the customer usually goes through and a whole set of complementary information about each stage.
1. Preparation:
a. Select the customer profile and scope
b. Collect and analyze existing information about customer expectations, questions, and complaints.
c. Identify information gaps on each status and build a plan for collecting the missing information (VOC – Voice of Customer)
2. Build a Map of the Customer Journey:
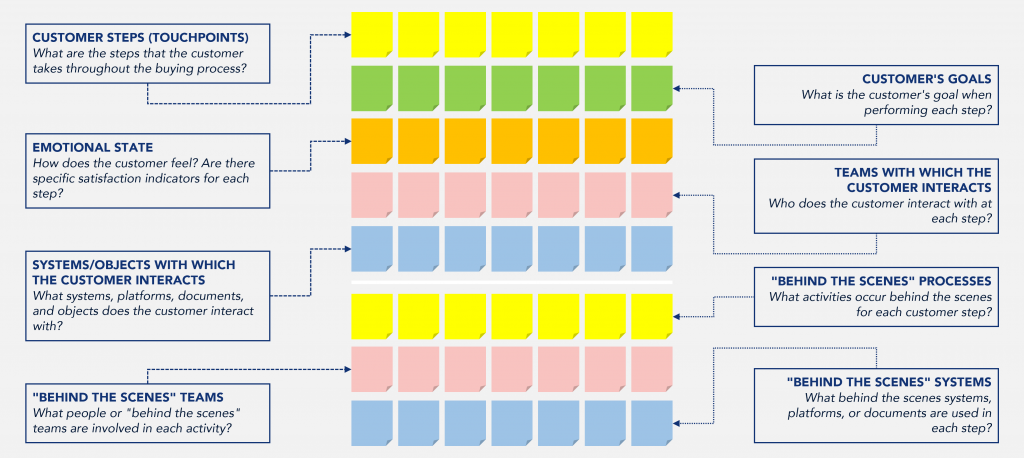
a. Analyze the customer’s steps or touchpoints during the buying journey. Consider all interactions (website, social networks, email, chatbots, phone, face-to-face, …). Set the steps as the first line of the customer’s buying experience map.
b. Identify the customer’s goals at each step. Understand what the customer is trying to achieve in each step. Multiple actions can have the same purpose. Place the information on the map.
c. Gather information about the customer’s attitudes and emotions at each step. Identify how the customer feels: satisfied, happy, excited, sad, and nervous, among others. Enter the information about the customer’s emotions into the map. If there is information on customer satisfaction metrics by stage or about complaints, include them.
d. Identify who interacts with the customer during the journey. Put the people, groups, or teams with whom the customer interacts at each step on the map.
e. Understand what platforms, systems, documents, or objects the customer interacts with at each step. Incorporate all the information into the map.
f. Identify where the points of conflict are and where the customer feels uncomfortable. Score each step. Add the information to the map.
g. Understand the behind the scenes activities. Identify on the map what activities happen in the areas that do not have direct contact with the customer for each step identified above.
h. Clarify who the people or teams involved behind the scenes are in each step. Add the information to the map.
i. Identify the systems and platforms used behind the scenes in each step. Add the information to the map.
3. Priorities Definition:
a. Define improvement priorities. Start by improving the points that cause the most conflict and pain for the customer. If multiple points in the customer journey have high scores, use the Effort (Difficulty) vs. Impact (Benefit) Matrix and start with the points with the most benefit and least effort.
How to Improve the Customer Experience?
Use the Customer Experience Canvas to start improving the customer’s buying journey. For each priority opportunity, fill in the templates.
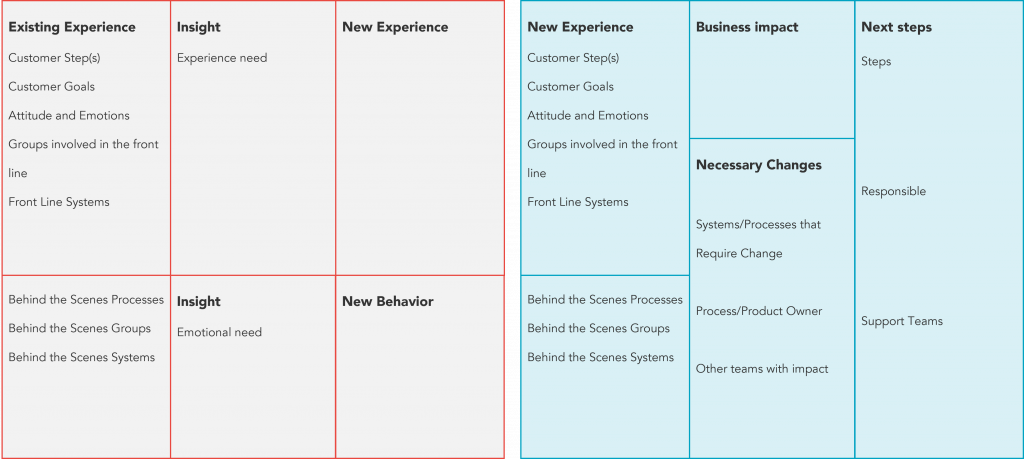
- Fill in the “Existing Experience” information based on the buying journey map.
- Provide information on “Insights” into the customer’s needs. Understand what the customer needs to satisfy their needs.
- Design the “New Experience.”
- Define the “New Attitudes” and “New Behaviors” you want to trigger in the customer.
- Calculate the “Business Impact” and the financial impact and return on investment if possible.
- Define the “Necessary Changes” to implement the vision. Identify who is needed to make the change.
- Define what “Next Steps” need to be taken, who will lead the change, and who will help.
Indicators for Measuring Customer Satisfaction
Indicators for measuring customer satisfaction are measures used to quantify how satisfied or dissatisfied the consumer is with their relationship with the company. These indicators encompass everything that involves the customer’s buying journey.
The satisfaction indicators allow us to have a broader and more realistic view of the customer’s perception regarding the experience provided by the company. These indicators can be defined for specific touchpoints or the experience as a whole.
The quality of the experience influences the buying decision, the way the customer will talk about the brand to other people, and their loyalty. In other words, it is vital to understand how satisfied the customer is throughout the journey.
These indicators also help define priorities for improvement, as they allow you to identify where the most significant pain points are.
There are several indicators to measure customer satisfaction.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric that allows you to measure customer satisfaction and loyalty towards companies, regardless of the type of activity. The critical question is: On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague?
Scores of 0 to 6 are classified as detractors. These customers indicate that their lives have worsened after purchasing the product or service from the company mentioned. They criticize the company publicly and will probably not do business with it again, except in extreme situations.
Scores of 7 and 8 are classified as neutral customers. These customers buy only those products and services that are needed. They are not loyal and are not enthusiastic about the brand or company.
And finally, 9 and 10 are classified as promoters. These customers have a better life after the start of the relationship with the company. They are loyal, offer positive feedback, and promote the company or brand.
The score is calculated by subtracting the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters.
Customer Effort Score (CES)
The Customer Effort Score (CES) measures customer effort during interactions with the brand. The more work, a consumer, has to go through to buy a solution, ask a question, or solve a problem, the more dissatisfied they will be. The critical question of this indicator is: On a scale of “very easy” to “very difficult,” how easy was it to relate to our company?
CES should be measured immediately after the action one wants to measure. By postponing the assessment, there is a high probability that the customer will forget how they felt and give a false answer or ignore the assessment. CES is generally used after a purchase or subscription to a service or after interaction with a brand touchpoint. The CES scale can be a numeric, qualitative, or emoticon scale.
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT)
The Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) is a metric used to measure customer satisfaction with the company and at different stages of their journey.
It can be applied to assess various factors of the customer’s touch points with the brand.
The key questions are: How satisfied are you with the service you just received? How satisfied are you with the delivery time of our product? What is your level of satisfaction with the results obtained from our solution?
The customers must evaluate the questions and give scores ranging from 1 to 5, or 1 to 10, on a scale where 1 is “totally dissatisfied” and 5 or 10 is “totally satisfied.” The possibility of using alternatives (terms, not numbers) is also possible.
The Impact of an Improved Buying Experience
A positive buying experience is crucial to business success because a happy customer will likely become a loyal customer and brand promoter. The best marketing a company can have is a customer who promotes the business through word-of-mouth marketing and advocates the brand and the products or services.
How you think about the customer experience probably profoundly impacts how you look at the business as a whole.
As shown, the first step in improving customer experience is mapping it and collecting data to identify opportunities. Improving pain and dissatisfaction points can involve several solutions, from improving the omnichannel experience and customer service standards using a CRM, or any other solution that positively impacts the customer.
See more on Sales & Marketing
Find out more about improving this business area
