Introduction to Lean Management
Lean Management represents a disruptive management philosophy, advocated by the Kaizen Institute, aiming for operational excellence through the elimination of all waste. In the current economic ecosystem, marked by increased competition and a relentless quest for efficiency, this approach provides businesses with an undeniable competitive edge. By focusing on creating added value for the customer while optimizing available resources, Lean Management emerges as a fitting response to the complex challenges of the modern business world.
Definition of Lean Management
Lean Management, or Lean, is defined as a systematic set of methods for improving processes by identifying and eliminating waste not only in production but also in all aspects of the company. This approach is distinguished by its orientation towards the value perceived by the customer, constantly seeking to increase quality, reduce lead times, and decrease costs. It is a philosophy that encourages continuous improvement and the involvement of all employees, from operators to the executive team.
Origins of Lean Management
From Toyota to the World
The origins of Lean Management trace back to the Toyota Production System (TPS), established by Taiichi Ohno and Eiji Toyoda in the post-war years. The TPS was designed to eliminate waste and optimize efficiency in the automobile production process, with principles such as Just-In-Time (JIT) and autonomation, promoting demand-driven production and minimizing inventory. This method quickly proved its value, transforming Toyota into a global leader in the automotive industry.
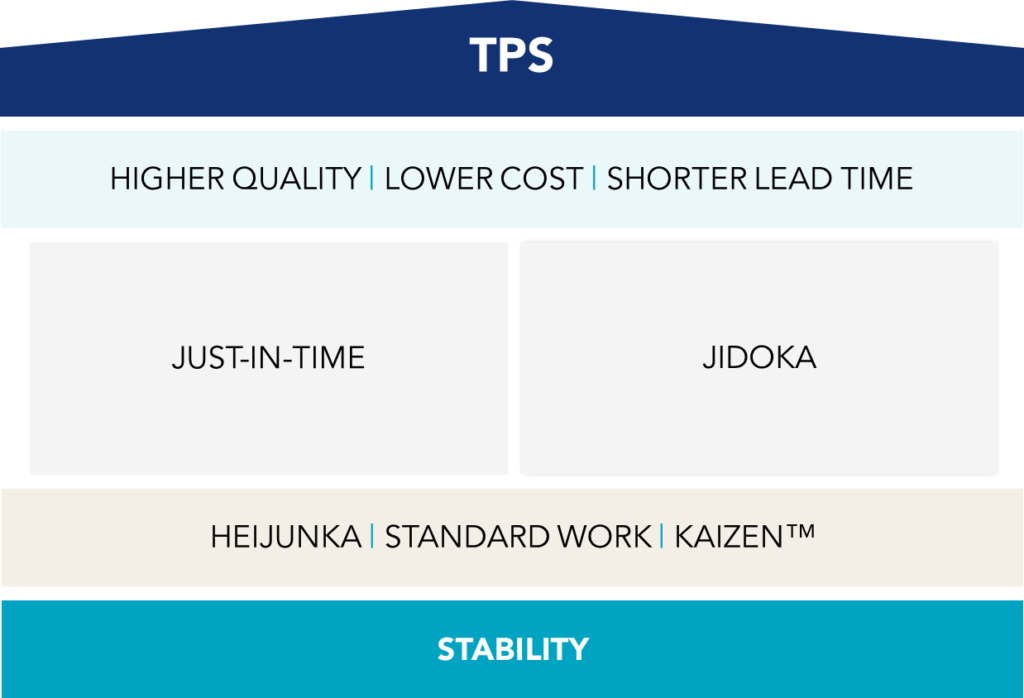
Evolution Over the Decades
Over the years, Lean Management has transcended the boundaries of the automotive industry to be implemented in various sectors, from production to services, healthcare, and technology. This evolution has seen the integration of new practices and tools, notably Lean Six Sigma, enriching the Lean approach with a qualitative and quantitative dimension. Today, Lean Management is considered a comprehensive management philosophy, applicable to any organization seeking to improve its overall performance.
Why Lean is Crucial for Modern Businesses
In an economic context where agility and efficiency are the keys to success, Lean Management proves to be an essential lever for companies eager to maintain a cutting-edge in their sector. With its focus on waste reduction and continuous improvement, it allows organizations to respond more swiftly to the changing needs of customers, enhance the quality of their products and services, all while reducing operational costs. Furthermore, by promoting a culture of engagement and employee empowerment, Lean facilitates innovation and collaboration, fundamental elements for the sustainable development of businesses in an increasingly competitive environment.
Fundamental Principles of Lean Management
Lean Management is based on five fundamental principles that form the cornerstone of this philosophy. These principles guide companies in their quest for efficiency, continuous improvement, and maximizing value for the customer.
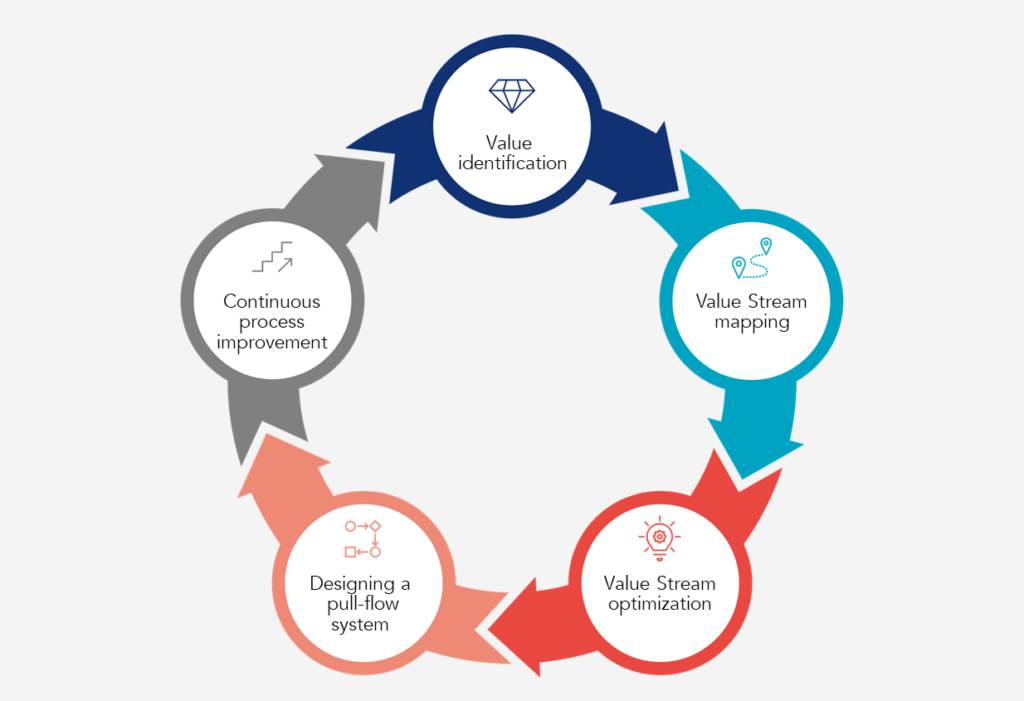
Identification of Value
Everything starts with a precise understanding of what the customer considers as value. This crucial step involves a detailed analysis of customer needs and expectations to ensure that the company focuses on what is truly important. By defining value from the customer’s perspective, companies can streamline their processes and eliminate what does not add value.
Value Stream Mapping
After identifying value, it is essential to visualize all the processes (the value stream) that contribute to the creation of this value. This mapping covers all stages of the process, highlighting superfluous activities that do not contribute to added value. The goal is to have a clear vision of the production or service flow to identify and eliminate waste.
Creation of a Continuous Flow
Optimizing the value stream aims to make production or service processes as smooth as possible. By eliminating interruptions, delays, and bottlenecks, companies can ensure a continuous flow that reduces cycle times and increases flexibility. A continuous flow also allows for a quicker response to customer demands and improves overall quality.
Establishment of a Pull System
Unlike traditional push production systems based on forecasts, Lean Management promotes a pull system. In this system, production is directly triggered by customer demand, minimizing inventory, and reducing waste. This principle aims to produce only what is needed, when it’s needed, and in the necessary quantity.
Pursuit of Perfection
The pursuit of perfection underlies the entire Lean Management philosophy. It means continuous improvement of processes, products, and services. Cultivating a culture where all employees are encouraged to identify improvement opportunities, companies can innovate continuously and maintain their competitiveness. The pursuit of perfection also involves adapting to market changes and new technologies to constantly improve the value offered to customers.
These fundamental principles of Lean Management, when applied consistently and methodically, enable companies of all sizes and from all sectors to achieve superior levels of operational efficiency.
Lean Management Tools
In the framework of Lean Management, a plethora of tools and methodologies has been developed to support the application of its fundamental principles. These tools aim to identify and eliminate waste, improve the quality and efficiency of processes, and maximize value for the customer.
The Six Sigma Methodology
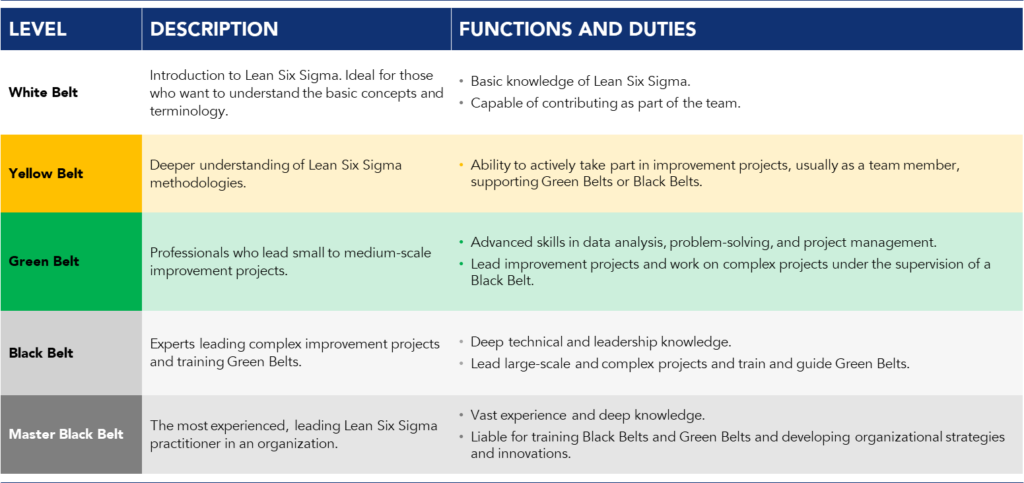
Six Sigma is a rigorous and disciplined methodology that uses statistical data to improve processes and eliminate defects. By combining Lean Management and Six Sigma, companies adopt a powerful approach, known as Lean Six Sigma, aimed at accelerating performance improvement by reducing process variability. Professionals trained in Lean Six Sigma Belts, from white belt to master black belt, are key players in implementing this methodology.
The 5S Method
The 5S represents a technique for organizing the workspace to improve efficiency and safety. The five steps – Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain – lead to an optimized work environment promoting better operational performance.
The Kaizen Method
Kaizen, meaning “continuous improvement” in Japanese, is at the heart of Lean Management. This approach engages every employee, from the executive team to the operators, in the continuous search for small daily improvements. The goal is to cultivate a corporate culture where continuous improvement is embedded in daily behavior.
The SMED Method
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) is a technique designed to drastically reduce changeover time. By minimizing conversion delays, companies can improve their production flexibility, reduce manufacturing batches, and respond with more agility to the customer’s demand.
The Kanban Method
Kanban is a visual production management system aiming to control the work in progress using cards (or digital alternatives) to signal the need for component replenishment. This tool helps avoid overproduction and minimize inventory by closely aligning production with the actual demand.
Other Essential Tools
- JIT (Just-In-Time): A strategy aiming to improve production flow by producing and delivering only what is needed, when it’s needed, and in the necessary quantity.
- Gemba: The Gemba Walk involves going to the place where work is done to observe, understand, and improve processes.
- Poka-yoke: An error-proofing system that helps avoid defects in the production process.
- VSM (Value Stream Mapping): A tool for visualizing the flow of materials and information through all production stages to identify and eliminate waste.
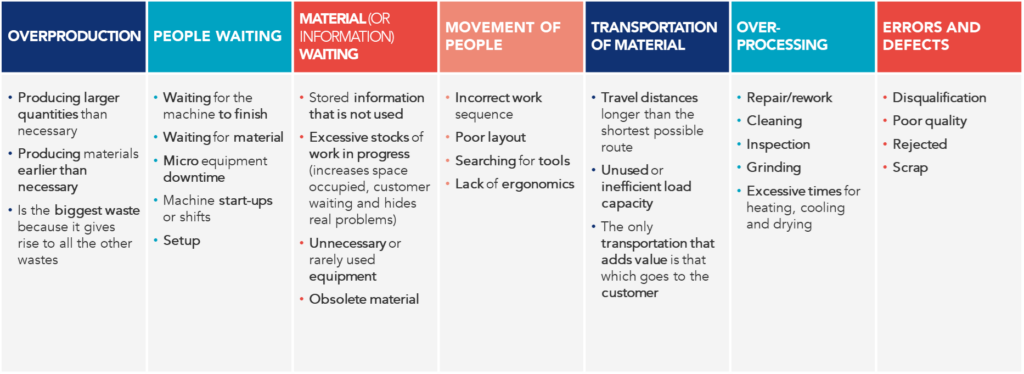
- Muda: A Japanese term for “waste,” referring to activities that do not add value from the customer’s perspective. There are seven types of Muda, represented in the image below.
Adopting these Lean Management tools, coupled with adequate Lean training and Lean Six Sigma certifications, allows companies to make significant strides in their quest for operational excellence. By integrating these practices, organizations can not only improve their internal processes but also strengthen their competitiveness in the market.
Lean Manufacturing Management: Strategies and Practices
Lean Manufacturing Management is a specific application of Lean Management in the production sector. Drawing from the fundamental principles of Lean, this approach aims to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and increase quality in production processes.
Principles of Lean Applied to Manufacturing
Within Lean Manufacturing, the principles of Lean Management are adapted to the specificities of the production environment. Identifying value is done according to the strict criteria of quality, cost, and delivery time required by the customer. Value stream mapping becomes an essential tool for visualizing production processes and identifying sources of waste. Creating a continuous flow and establishing a pull system optimizes production by reducing unnecessary inventory and responding with enhanced flexibility to demand. The pursuit of perfection is a constant commitment to improving processes and products.
Examples of Success and Evolution in Manufacturing
Numerous companies worldwide have transformed their production operations through Lean Manufacturing. For example, Toyota has continued to refine its production system, becoming a global model of efficiency. Other companies, such as GE (General Electric) and Intel, have also embraced Lean Manufacturing to improve their products’ quality, reduce time to market, and lower production costs. These successes demonstrate Lean Manufacturing’s adaptability and evolution according to the specific needs of each and every industry.
Integration of Modern Technologies and Lean Manufacturing
The integration of modern technologies has become a central pillar of Lean Manufacturing. Digital tools for workflow automation or Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) allow better visibility and increased control over production processes. The Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics offer new opportunities to minimize waste and improve efficiency. For instance, using smart sensors can reduce downtime by predicting failures before they occur, while collaborative robots can work alongside humans to perform repetitive or dangerous tasks, thus enhancing safety and productivity.
Lean Manufacturing, enriched by these technologies, enables companies to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving industrial environment.
Objectives and Benefits of Lean Management
Lean Management is more than just a management methodology, it is a philosophy that redefines how a company operates. The objectives and benefits of this approach are many, positively affecting all aspects of the organization. Below are some examples of these benefits.
Efficiency Improvement
One of the main objectives of Lean Management is the continuous improvement of operational efficiency. By applying principles such as creating a continuous flow and establishing a pull system, companies can significantly reduce downtime and increase their productivity. This translates into an enhanced ability to respond quickly to customer demands and adapt to market changes while maintaining high quality levels.
Cost Reduction
Lean Management also aims to reduce production costs by eliminating waste in all its forms, whether overproduction, waiting time, unnecessary transport, inappropriate processes, excess inventory, non-ergonomic movements, or manufacturing defects. By focusing on value-adding activities, companies can minimize expenses and improve profitability. This systematic approach leads to substantial savings, allowing companies to reinvest in innovation and growth.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction and loyalty are at the heart of Lean Management’s objectives. By emphasizing value creation for the customer, this philosophy helps companies to better understand and meet customer needs and expectations. The results are higher-quality products and services, delivered faster and at a lower cost. This continuous improvement of the offering strengthens customer satisfaction, a crucial competitive advantage in today’s environment.
Quality Improvement
By adopting Lean Management, companies benefit from increased quality of their products and services thanks to the elimination of non-essential processes and the focus on those that generate value.
Positive Corporate Culture
Lean Management promotes a culture of collaboration, employee empowerment, and collective problem-solving. This positive culture results in better team motivation, improved communication, and greater engagement with the company’s objectives.
In summary, Lean Management offers a multitude of benefits, ranging from operational improvement and cost reduction to increased customer satisfaction and an enriched corporate culture. These advantages make Lean an indispensable approach for companies seeking to excel in an increasingly competitive market.
Training and Development in Lean Management
The success and sustainability of a Lean strategy within an organization largely depends on continuous training and the development of a deeply rooted Lean culture. The Kaizen Institute, recognized for its expertise in Lean Management, plays a leading role in supporting companies in this transformation process. Training and development in Lean Management are designed to equip professionals with the tools and skills necessary to initiate, implement, and support Lean initiatives within their organizations.
Training Programs
The Lean training programs offered by the Kaizen Institute cover a wide range of levels and areas, from the fundamental principles of Lean and Kaizen to advanced Lean Six Sigma techniques. These trainings are structured around several certification levels, including Lean Six Sigma belts, allowing participants to progress through a structured learning journey according to their experience and needs.

The training includes not only theoretical sessions but also practical workshops and real case studies, thus facilitating the application of acquired knowledge in a concrete professional context. The goal is to develop problem-solving skills, process optimization, and project management, based on Lean principles.
Developing a Lean Culture
Beyond technical training, establishing a Lean culture within a company is crucial for the long-term success of Lean initiatives. This culture is built on several pillars, including the commitment of the executive team, the active participation of all employees, open communication and knowledge sharing, and the recognition of individual and collective contributions to continuous improvement.
The Kaizen Institute emphasizes the importance of training leaders capable of guiding their teams in the continuous improvement process and solving problems effectively. This involves training leaders at all organizational levels to promote Lean values, train employees in Lean tools, and create an environment conducive to innovation and efficiency.
In conclusion, training and development in Lean Management are essential components of organizational transformation towards operational excellence. Through targeted training programs and the promotion of a Lean culture, companies can achieve significant improvements in efficiency, quality, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction. The Kaizen Institute positions itself as a key partner in this transformation journey, offering expertise, resources, and support necessary for the successful implementation of Lean Management.
Still have some questions about Lean Management?
What is the importance of leadership in the success of Lean Management?
Leadership plays a crucial role in the success of Lean Management, as it involves much more than just the simple implementation of methods and tools, it is a cultural transformation of the organization. Lean leaders inspire and guide their team towards continuous improvement, focusing on creating value for the customer and eliminating waste. They must not only deeply understand the principles of Lean but also embody them daily, encouraging communication, team problem-solving, and employee empowerment.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that combines the principles of Lean Management, focused on waste reduction and process flow improvement, with those of Six Sigma, which focus on reducing variability and improving quality through statistical analysis and problem-solving techniques. This integrated approach aims to maximize operational efficiency and product or service quality by using a structured set of tools and techniques to identify and eliminate defects, delays, and inefficient processes.
See more on Lean
Find out more about improving this business area
See more on Operations
Find out more about improving this business area
