Continuous improvement
Starting a journey towards continuous improvement requires more than simply adopting methodologies; it demands a cultural shift that involves every aspect of an organization. By internalizing the Kaizen principles of incremental change, companies can benefit from the full potential of their workforce, fostering an environment where every employee participates in the transformation. This shift sets the stage for strategic and operational improvements, from optimizing setup times and production sequencing to enhancing process flows. These incremental improvements and continuous adjustments are essential for improving efficiency and quality to remain relevant and competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
Embracing a Continuous Improvement Culture
Adopting a continuous improvement culture is fundamental to achieving operational excellence within organizations. This approach is not just a business strategy but a philosophy that involves all seniority levels, encouraging innovation and efficiency. The KAIZEN™ principles lay the foundation of this culture, promoting an environment where small, continuous improvements lead to significant gains in performance, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Incorporating KAIZEN™ principles into organizations means engaging all employees, from top management to front-line workers, in identifying and solving problems. This approach views continuous improvement as a shared responsibility, valuing everyone’s contributions and reinforcing the commitment to shared objectives.
Organizations must also invest in their employees’ ongoing training and development to sustain this culture. Empowerment through methodologies like Lean Management maximizes individual skills and ensures the entire team is aligned with efficiency, quality, and continuous improvement.
Companies establish a solid foundation for innovation and success by embracing a continuous improvement culture. Committing to operational excellence improves the efficiency and quality of internal processes and strengthens market competitiveness.
Next, we discuss how continuous improvement can transform organizations’ strategic and operational dynamics.
Implementing Continuous Improvement: Strategies and Techniques
Continuous improvement is a fundamental concept within operational excellence and refers to the systematic and constant effort to improve an organization’s processes, services, and products.
Continuous improvement is an endless cyclical process, highlighting the importance of a proactive problem-solving and process optimization approach. This concept is based on the idea that there are always opportunities for improvement, no matter how efficient or advanced current systems are. Therefore, the target is not just fixing specific faults or problems but cultivating an environment where the pursuit of excellence is constant.
The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle assists with implementing these continuous improvement initiatives. It is an iterative cycle that provides a framework for implementing and evaluating changes. By following this model, organizations can ensure their improvement strategies are systematically planned, tested, evaluated, and optimized, promoting continuous and sustainable evolution.
This cycle provides the necessary structure for implementing continuous improvement and ensures that these initiatives are conducted effectively, resulting in tangible benefits for the organization.
PDCA Cycle: The Core Methodology for Continuous Improvement Processes
The PDCA Cycle outlines the foundation for continuous improvement initiatives in organizations aiming for operational excellence. This methodology offers an iterative structure facilitating systematic improvement implementation, allowing organizations to test changes on a small scale before applying them broadly. This cyclical approach allows continuous adjustment of processes, products, and services based on actual data and honest feedback.
Plan: This phase involves identifying an improvement opportunity and developing a detailed action plan to address it. It includes setting clear objectives, selecting success indicators, and formulating hypotheses about how the proposed changes could result in improvements.
Do: Here, the planned changes are implemented on a small scale or in a controlled environment. This step allows organizations to test the viability of the proposed solutions without significantly disrupting daily operations.
Check: After implementation, the results are carefully analyzed and compared with the objectives set in the planning phase. This step is crucial for assessing the effectiveness of the implemented actions and identifying any deviations or areas for improvement.
Act: Based on the observations and data collected, organizations decide whether the changes should be applied on a large scale, adjusted, or discarded. If the results are positive, the improvements are standardized and integrated as new practices. Otherwise, the cycle is restarted with new hypotheses and strategies.
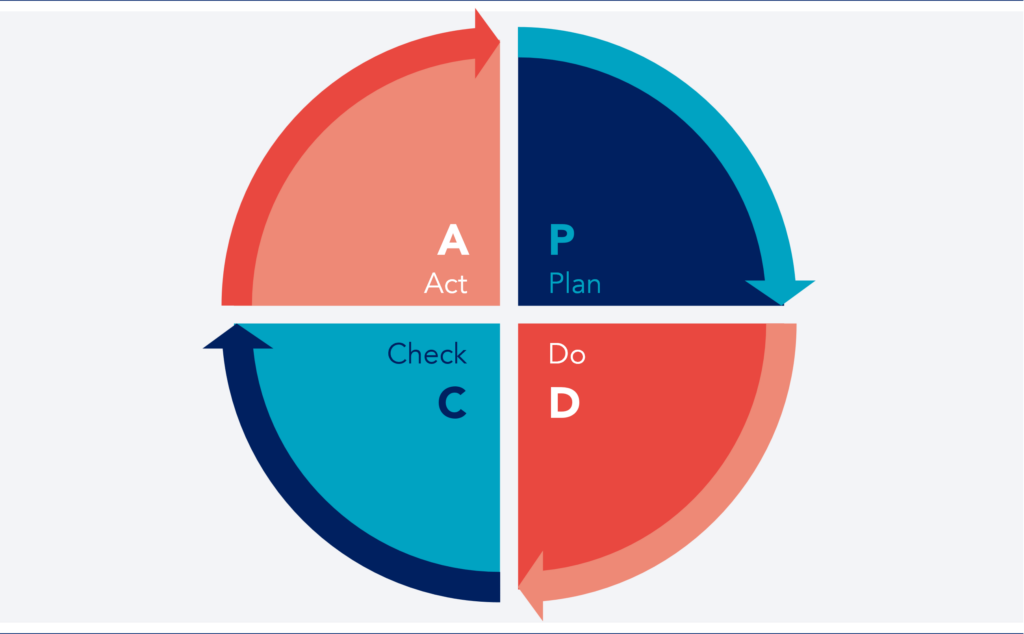
Applying the PDCA cycle fosters a culture of continuous learning and adaptation, enabling organizations to respond more effectively to market changes and demands. Furthermore, this tool supports the implementation of other continuous improvement strategies and techniques, such as agile methodologies, 5S, Kanban, and Total Quality Management (TQM).
Agile Methodology
Adopting Agile allows organizations to respond quickly to market changes and customer demand. This methodology emphasizes collaboration, adaptability, and iterative development, allowing teams to implement improvements more efficiently and effectively.
5S Methodology
Originating from Japan, the 5S methodology focuses on organizing and cleaning the workspace. By following the five steps – Sort (Seiri), Set in order (Seiton), Shine (Seiso), Standardize (Seiketsu), and Sustain (Shitsuke) – organizations can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and create a safer and more productive working environment.
The Kanban Method
This visual management technique for controlling work as it moves through processes is beneficial for managing and improving continuous workflows. Kanban helps teams visualize work, limit work in progress, and optimize workflow efficiency.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is a comprehensive approach to quality management that promotes product and service quality improvement through cultural and operational transformation across the organization. It involves everyone in continuous improvement and emphasizes customer satisfaction.
Successful implementation of these continuous improvement strategies and techniques depends on selecting the appropriate methodologies and the organization’s ability to cultivate a mindset that values learning, innovation, and commitment to excellence. Continuous training and development of employees’ skills are essential to sustain improvement efforts and ensure initiatives are effective and aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Continuous Improvement Across Industries
Applying continuous improvement transcends the boundaries of specific sectors, showing its relevance and adaptability across a wide range of industries. Continuous improvement supports innovation, operational efficiency, and competitiveness from manufacturing to service-based industries. The ability to adapt and implement these practices in different contexts not only highlights the universality of the concept but also underscores the importance of customized strategies tailored to the unique needs and challenges of each sector.
In the manufacturing sector, for example, implementing continuous improvement practices is crucial for increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and improving product quality. Lean and Six Sigma methodologies are often applied in this context to optimize processes and eliminate variability, resulting in leaner operations and higher-quality products.
On the other hand, in the service sector, continuous improvement focuses on optimizing service delivery processes and improving customer experience. Practices such as Business Process Management (BPM) and implementing Quality Management Systems (QMS) help organizations offer efficient services that meet customer expectations.
Regardless of the industry, effective continuous improvement implementation requires a holistic approach that considers the technical aspects of operational processes and human and cultural elements. The involvement and commitment of all organizational levels are crucial for success.
Operational Excellence in Manufacturing
Achieving operational excellence in manufacturing is a continuous journey based on implementing continuous improvement practices to optimize processes, maximize efficiency, and elevate product quality. This approach allows organizations to respond more effectively to market dynamics and customer expectations and contributes to long-term business sustainability.
Applying Lean, Six Sigma, and KAIZEN™ frameworks in the manufacturing environment has proven effective in identifying and eliminating waste, reducing process variability, and promoting a continuous improvement culture. These strategies help companies optimize resource use, minimize operational costs, and improve customer satisfaction while ensuring compliance with strict quality standards.
Another key component of operational excellence in manufacturing is the ability to integrate technology and innovation into production processes. Adopting advanced technologies, such as automation, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT), allows for greater precision, efficiency, and flexibility in production. These technologies facilitate real-time monitoring and control of processes and enable organizations to adapt rapidly to changes in production or market demand.
Beyond incorporating technology, operational excellence requires continuous employee skills development. Training and engaging employees are vital to cultivating a mindset focused on innovation, quality, and efficiency. By empowering employees to identify improvement opportunities and actively participate in the continuous improvement process, organizations foster an environment contributing to innovation and excellence.
In these circumstances, quality management is essential in ensuring all aspects of production are meticulously monitored and optimized to meet or exceed quality expectations. Implementing quality management systems allows for systematic process evaluation, identifying improvement areas, and implementing practical solutions to safeguard product consistency and quality.
As manufacturing focuses on optimizing and ensuring product quality, organizations face the challenge of continuously improving service delivery. Adapting continuous improvement practices to the service context increases operational efficiency and enhances customer experience. Effective manufacturing strategies offer valuable insights for service optimization, highlighting operational excellence links with various business aspects.
Enhancing Service Delivery through Continuous Improvement
Optimizing service delivery through continuous improvement is essential for organizations aiming to meet and exceed customer expectations. In an increasingly competitive business environment, offering high-quality services efficiently is a significant competitive advantage. Implementing continuous improvement practices in the service sector involves optimizing service delivery processes, improving customer experience, and ensuring agile and adaptable service delivery.
The approach to continuous service improvement often focuses on understanding customer needs and expectations and using this information to optimize processes. This approach may involve reviewing and refining customer touchpoints, simplifying procedures to increase efficiency, and implementing feedback systems that allow quick and informed adjustments.
In this context, technology also plays a crucial role in improving service delivery, offering tools for task automation, customer data collection and analysis, and effective communication. Data analytics tools, for example, can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences, enabling organizations to customize their service offerings and anticipate future customer needs.
Commitment to continuous improvement allows service sector organizations to adapt rapidly to customer expectations and changes in the market environment. Organizations maintain competitiveness and relevance in today’s dynamic market by improving existing processes and anticipating and adapting to future changes.
The Future of Continuous Improvement in Business
As the business environment evolves at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological progress, shifts in consumer expectations, and the emergence of new business models, the future of continuous improvement is both challenging and bright. In this sense, continuous improvement is a fundamental survival and business development strategy for the future.
Digitalization and automation are increasingly present in continuous improvement strategies, offering new opportunities to optimize processes, improve accuracy, and increase operational efficiency. Integrating technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and advanced data analytics enables a deeper understanding of business processes and data-driven decision-making, anticipating problems before they occur and identifying innovation opportunities.
Furthermore, sustainability is becoming critical in continuous improvement as organizations acknowledge the importance of operating responsibly and sustainably. Integrating sustainability practices into continuous improvement processes contributes to environmental and social well-being and offers competitive advantages by improving resource efficiency and strengthening corporate reputation.
Continuous improvement is a strategy to face current challenges and prepare for future opportunities and challenges. In this context, the role of continuous improvement consultancy in facilitating and guiding organizations on this journey becomes even more relevant, providing support, knowledge, and the needed tools to achieve operational excellence in a constantly changing world.
Still have some questions about Continuous Improvement?
What is continuous improvement?
Continuous improvement, a core concept in pursuing operational excellence, refers to the systematic and relentless effort to optimize an organization’s processes, services, and products. This process is cyclical and never-ending, emphasizing the importance of a proactive approach to solving problems and optimizing processes. It is based on the premise that there are always opportunities for improvement, regardless of how efficient or advanced the current systems/processes are. In this sense, it is an organizational commitment to continuous growth and adaptation to market changes, guaranteeing long-term sustainability and competitiveness. In Lean Management, continuous improvement is also known as Kaizen.
What is the Relationship Between Continuous Improvement and Employee Engagement?
Continuous improvement and employee engagement are deeply interconnected. Implementing continuous improvement depends on employees’ active participation and commitment at all organizational levels. When employees are involved and feel in charge of the initiatives, the likelihood of successfully implementing improvements significantly increases. Moreover, engaging employees in continuous improvement contributes to their personal and professional development, increasing job satisfaction and promoting a more innovative and productive environment.
What is the Role of Technology in Advancing Continuous Improvement?
Technology is a critical enabler in advancing continuous improvement, providing the necessary tools for analyzing processes, identifying inefficiencies, and implementing solutions effectively. Modern technological solutions, such as big data, artificial intelligence, and automation, allow for more accurate data collection and in-depth data analysis, supporting identifying improvement areas. Additionally, technology can automate repetitive and time-consuming processes, freeing employees to focus on higher-value tasks, thus fostering innovation and increasing operational efficiency.
See more on People & Culture
Find out more about improving this business area
See more on Operations
Find out more about improving this business area
