In our fast-paced, ever-evolving business landscape, companies are always looking for ways to refine their operations and boost efficiency. Lean Six Sigma stands out as a robust solution, fostering continuous improvement for these organizations.
As companies push the boundaries in pursuit of exceptional performance, Lean Six Sigma offers a powerful toolkit and guiding principles that empower organizations to tackle challenges confidently. By merging the strengths of both Lean and Six Sigma methodologies, it paves the way for organizations to reduce waste, fine-tune processes, and elevate the quality of their products and services.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is an integrated and comprehensive approach to enhancing operational efficiency and quality. It merges two distinct methodologies, Lean and Six Sigma, to form an effective framework for continuous improvement.
Lean originates from the Toyota Production System and focuses on eliminating activities that do not add value to a process i.e. waste.
On the other hand, Six Sigma is a data-centric methodology aimed at systematically minimizing process defects. The name “Six Sigma” represents an aspirational quality level, aiming for a mere 3.4 defects out of a million opportunities. Six Sigma employs a rigorous statistical approach to pinpoint and address root causes to achieve this quality level.
Organizations harness the best of both worlds by integrating Lean and Six Sigma. While Lean streamlines processes by cutting waste and enhancing flow, Six Sigma uses data analysis to detect and eradicate problems at the source. Together, they provide a well-rounded approach to continuous improvement.
Lean Six Sigma vs Kaizen: main similarities and differences
Both Lean Six Sigma and KAIZEN™️ provide valuable methodologies for tackling organizational challenges, albeit with distinct approaches. They differ in some aspects, each offering unique perspectives on problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Six Sigma heavily relies on quantitative metrics and statistical analysis to drive improvements in business processes, aiming to minimize defects and enhance quality. On the other hand, KAIZEN™️ focuses on holistic improvement throughout the organization, transcending reliance solely on numerical data associated with quality.
Despite these methodological nuances, both Six Sigma and KAIZEN™️ share a common goal: to optimize corporate efficiency and effectiveness by purging non-value-added activities. In practice, companies can adopt a blended approach, incorporating elements from both Six Sigma and Lean concepts, as well as from KAIZEN™️.
Both Lean Six Sigma and KAIZEN™️ stand out as exceptional concepts that yield significant time and cost savings, providing organizations with valuable tools to enhance their operations.
Why is Lean Six Sigma important?
The Lean Six Sigma is important for several fundamental reasons that positively impact organizations. This comprehensive approach to continuous improvement provides significant benefits that are reflected in various key areas:
Operational Efficiency Reach
The Lean Six Sigma is designed to eliminate waste, reduce inefficiencies, and optimize processes. This leads to more streamlined workflows, shorter cycle times, and a more efficient use of resources.
Quality Improvement
The Six Sigma methodology aims to reduce defects and enhance quality. This results in higher-quality products and services, reducing customer complaints, rework, and costs associated with errors.
Increased Customer Satisfaction
Lean Six Sigma enhances customer satisfaction by focusing on quality, reducing lead time, and delivering value to the customer.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Lean Six Sigma employs statistical analyses for informed decision-making. This diminishes subjectivity in business decisions, allowing organizations to identify and address the root causes of problems more effectively.
Cost Reduction
Lean Six Sigma significantly reduces operational costs by eliminating waste, rework, and defects. This directly improves profit margins and competitiveness.
Implementation of a Culture of Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement throughout the organization. Employees are empowered to identify issues, implement solutions, and seek excellence in their daily processes. They are also encouraged to discover new ways of doing things, which can lead to innovative products, services, and processes.
Lean Six Sigma provides a structured and systematic approach to enhancing efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction while driving a culture of continuous improvement and data-driven decision-making. Organizations that successfully implement Lean Six Sigma often gain a significant competitive advantage.
What are the Principles of Lean Six Sigma
The values of Lean Six Sigma are based on a combination of Lean and Six Sigma principles. The following are the main principles:
Focus on Customer Needs
All improvement efforts should be directed toward delivering products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Waste Identification and Elimination
Tasks that do not add value from the customer’s perspective should be identified and eliminated.
Continuous Improvement
The pursuit of excellence is an ongoing process. Organizations should continuously seek ways to enhance their processes.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Decisions should be based on concrete analyses and data, not on assumptions. This approach aids in identifying root causes and assessing changes’ impact.
Employee Involvement
Employees are a valuable knowledge source on processes and challenges. Encouraging their active participation and involvement helps pinpoint improvement opportunities, and fosters shared accountability.
Process Standardization
Establishing clear and consistent standards for processes helps reduce variability and ensures product or service quality. Consistent processes also make it easier to detect anomalies.
Systematic and Structured Approach
Lean Six Sigma employs a systematic approach, such as the DMAIC methodology (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control), to address issues and roll out improvements.
Leadership and Commitment
Organizational leadership plays a pivotal role in fostering a continuous improvement culture.
Measurable Outcomes
The success of Lean Six Sigma is gauged through tangible outcomes, such as defect reduction, efficiency/productivity enhancement, cost savings, and customer satisfaction. Routine measurement ensures that improvements have a positive impact.
These principles guide Lean Six Sigma’s successful implementation, setting organizations to achieve sustainable improvement in their operations and processes.
The Lean Six Sigma Methodology
As previously mentioned, Lean Six Sigma is a structured and systematic approach that combines Lean and Six Sigma principles to achieve operational excellence and continuous improvement in organizations. It provides a clear and directed path for problem-solving and process improvement, addressing waste elimination.
DMAIC: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control
The DMAIC process is at the heart of the Lean Six Sigma methodology. It is a five-step sequence that guides teams in problem-solving and process improvement.
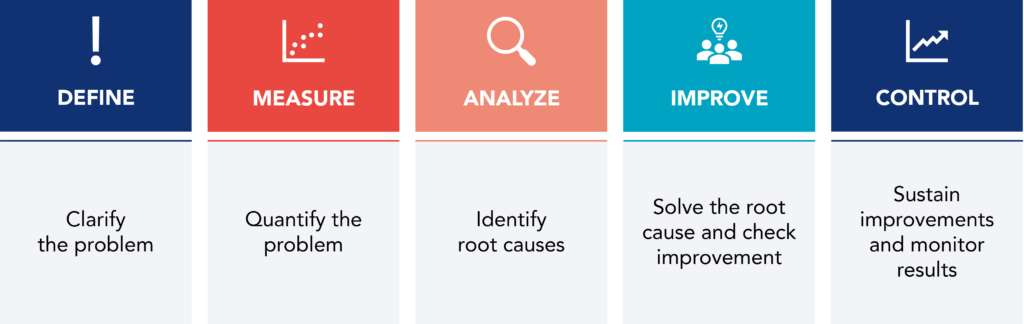
Each step plays a specific role in the transformation process:
- Define: In this step, the team clearly defines the problem and establishes improvement objectives. Understanding the current situation, identifying stakeholders, and setting success criteria are essential.
- Measure: During this phase, the team collects relevant data about the process. Measurement is vital to understand current performance, identify variations, and determine the extent of existing problems.
- Analyze: The analysis stage involves delving into the data gathered in the previous step to identify root causes. Statistical tools are often employed to identify patterns and trends that might be contributing to the issue.
- Improve: By understanding the root causes, the team develops and implements solutions. These are tested and adjusted as needed before final implementation.
- Control: The final step focuses on maintaining and monitoring the improvements. Control systems are established to ensure that changes remain effective in the long run. This involves defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and creating a monitoring plan.
How Lean Six Sigma is applied in real-world scenarios
Implementing Lean Six Sigma in real-world scenarios is adapted based on the organization’s specific needs and the problem at hand. Teams are established, typically with a Green or Black Belt leader who is an expert in the methodology.
Teams go through the DMAIC stages, applying specific tools and techniques at each phase. This might encompass data analysis, value stream mapping, and design of experiments, among others. The methodology is versatile enough to find applications in diverse sectors, from manufacturing to services.
Lean Six Sigma fosters a collaborative approach, engaging team members and relevant stakeholders throughout the process. The emphasis on data collection and analysis supports informed decisions, while the continuous improvement culture encourages experimentation and innovation.
Ultimately, Lean Six Sigma results in sustainable improvements in processes and quality, cost reduction, heightened customer satisfaction, and an organizational culture geared toward excellence.
What are Lean Six Sigma Tools
Lean Six Sigma boasts a wide range of tools and techniques that assist in problem identification, data analysis, problem resolution, and continuous improvement. These tools are employed throughout the DMAIC process stages to guide teams in systematically addressing issues. Here are some of the primary tools:
Value Stream Mapping
A visualization tool for a process flow, used during Value Stream Analysis, which identifies value-adding and wasteful activities. It aids in waste elimination and process optimization.
Diagrams (Fishbone or Cause and Effect Diagram)
Utilized to find an issue’s potential causes, this diagram categorizes them into areas such as people, processes, equipment, materials, and environment.
Control Charts
These are employed to monitor a process’s performance over time. They assist in identifying variations and deviations from set targets.
Pareto Analysis
A tool for prioritizing the most significant problems or causes and identifying the main contributors to a given problem.
Root Cause Analysis
Design of Experiments (DOE)
Used to test multiple process variables and reveal which factors have the most significant impact on process outputs.
Scatter Plots
These display the relationship between two variables and assist in finding a potential correlation between them.
Regression Analysis
Employed to examine the relationship between independent and dependent variables, allowing for outcome predictions based on historical data.
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Evaluates potential failure modes in a process or system, identifying their causes and impacts, and setting priorities for mitigation actions.
5S
An approach to workplace organization and cleanliness focused on enhancing efficiency, safety, and employee motivation.
Kanban
A visual workflow management tool that helps control and optimize production and material flow.
Poka-Yoke
Devices or techniques designed to prevent errors and defects, minimizing the potential for human mistakes.
These are just a handful of the many tools Lean Six Sigma offers. Which tool to use depends on the problem’s nature and the project’s unique needs. By smartly combining these tools, teams can effectively pinpoint and tackle issues, achieving sustainable improvements and outcomes in organizational processes.
Lean Six Sigma Training and Certification
Appropriate training plays a pivotal role in effectively implementing Lean Six Sigma. It is essential to deeply understand the tools, techniques, and methods involved to make meaningful improvements in organizational processes and outcomes.
A Lean Six Sigma certification is a formal recognition for individuals who have shown expertise in using the methodology. This certification confirms that they have acquired the skills to lead improvement projects, apply statistical tools, and lead teams to achieve efficiency, quality, and reduce variability.
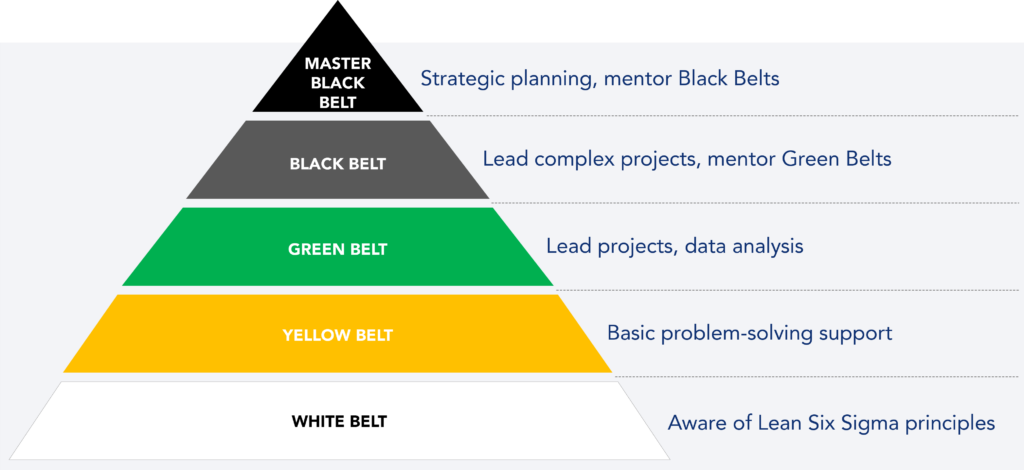
The most common certification levels – Lean Six Sigma Belts – are:
- White Belt: These are team members familiar with the basic concepts of Six Sigma and can support projects but do not hold a leadership role.
- Yellow Belt: They possess slightly advanced knowledge and can actively participate in projects as team members.
- Green Belt: These members have a deeper understanding of the Six Sigma tools and techniques and can lead small projects and collaborate closely with the Black Belts.
- Black Belt: These are highly trained and qualified project leaders. They are experts in Six Sigma and have the ability to lead complex improvement projects, apply advanced statistical tools, analyze data, and implement significant changes in processes.
- Master Black Belt: These seasoned experts lead in implementing and developing Six Sigma within the organization. They provide training, guidance, and support to Black Belts and Green Belts, ensuring the methodology is effectively applied throughout the organization.
Obtaining a certification in Lean Six Sigma typically involves completing formal training, knowledge examinations, and practical application of the skills learned.
The importance of training and certification in Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma training provides detailed knowledge of its underlying tools, methodologies, and principles. It empowers professionals to effectively identify problems, analyze data, and implement solutions, leading to measurable improvements.
Certification indicates that its holder possesses the necessary skills to apply Lean Six Sigma effectively. This ensures the right approaches are adopted to address complex issues and enhance processes.
On the other hand, Lean Six Sigma-certified professionals can spread a continuous improvement culture within their organizations. They can lead teams, foster collaboration, and guide implementing improvement initiatives.
How Kaizen Institute can help you become a Lean Six Sigma expert
The Kaizen Institute offers training programs with various certification levels to meet clients’ needs. Here are some benefits of the Kaizen Institute’s training and certifications:
- Specialized Training and Belt Certification: The Kaizen Institute provides hands-on training and certification at various levels. These programs cover all aspects of Lean Six Sigma, from basic concepts to advanced techniques.
- Globally Recognized Certification: The certifications provided by the Kaizen Institute are widely recognized internationally. Earning a Lean Six Sigma “belt” validates skills and knowledge, enhancing credibility as an expert in the field.
- Practical Experience: Beyond theory, the Kaizen Institute’s courses include hands-on exercises and real-world case studies. This allows participants to apply theoretical knowledge in actual scenarios and gain confidence in their abilities.
- Continuous Learning: The Kaizen Institute offers an ongoing learning journey, allowing professionals to deepen their knowledge in Lean Six Sigma as they advance in their careers.
Still have questions about Lean Six Sigma?
What is the fishbone diagram in Six Sigma?
The fishbone diagram, also known as the “Ishikawa Diagram” or “Cause and Effect Diagram”, is a visual tool used within Six Sigma to identify and analyze potential causes of a specific problem. It is called the “fishbone” due to its appearance, which resembles a fish’s spine when drawn.
The basic structure of the fishbone diagram consists of a central line from which several diagonal lines branch out, each representing a potential cause category. These categories typically fit into the renowned “6 Ms”:
- Methods: Processes, procedures, policies.
- Manpower: Skills, training, workforce.
- Machines: Equipment, tools, technology.
- Materials: Raw materials, supplies, inputs.
- Measurement: Data collection methods, evaluation.
- Environment: Conditions, context, workplace setting.
Each category is further divided into specific potential causes related to the problem.
What is the meaning of Kaizen?
“KAIZEN™️” is a Japanese word that means “continuous improvement.” Within the context of Lean Six Sigma and continuous improvement, the term “KAIZEN™️” describes a systematic and ongoing approach to enhancement and problem-solving in every aspect of an organization, from processes and products to culture.
See more on Lean
Find out more about improving this business area

