Capital projects play a crucial role in the development of organizations, requiring substantial investments and specialized resources. In this perspective, analyzing and applying lessons learned is a strategic tool to drive continuous improvement, knowledge sharing, enhanced risk management, and overall increased effectiveness and efficiency in future projects. Recognizing that each project is a unique source of learning, organizations can transform past experiences into incentives for progress, creating a continuous improvement culture that translates into strategic and operational advantages. This article explores how lessons learned correct past mistakes and actively shape the path to excellence in capital projects, representing a proactive approach to driving organizational excellence.
The Concept of Lessons Learned
The concept of lessons learned is based on extracting significant knowledge from past experiences, whether successes or challenges. In the context of capital projects, they cover various aspects, from operational processes to team dynamics and risk mitigation strategies.
A deep understanding of this concept involves identifying what went well and what could have been better and analyzing the underlying reasons. Each project has a unique narrative, filled with strategic decisions, overcoming obstacles, and innovative solutions. By translating them into lessons learned, organizations can document their history and forge a path for continuous improvement.
Furthermore, the concept of lessons learned transcends individual barriers, promoting a culture of knowledge sharing. Collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and other organizational units becomes crucial to enrich the collective work. Every project presents a unique opportunity for learning. By treating these lessons as a strategic resource, they become a catalyst for innovation, driving positive change and continuous improvement.
Benefits of Lessons Learned in Capital Projects
Systematically incorporating lessons learned in capital projects not only represents an improvement practice in management but also offers a variety of benefits:
- Standards and Process Improvement: Identify and understand what worked properly and where adjustments are needed to avoid repeating mistakes and increase productivity and quality.
- Risk Mitigation: Anticipate potential obstacles by analyzing past errors and implementing preventive measures to strengthen risk management.
- Informed Decision Making: Using the knowledge derived from lessons learned as a guide for better-informed decisions.
- Culture of Continuous Learning: Systematically spread lessons learned among teams and departments, developing more resilient and empowered employees.
Adopting a proactive approach to capture, analyze, and apply these lessons learned will ensure a solid foundation for the success of future projects.
Lessons Learned Workshop Steps
At the end of the project, conducting a lessons-learned workshop is a fundamental practice to extract valuable insights. This structured process consists of several steps to promote reflection, collaboration, and identifying areas for improvement.
Pre-workshop:
- Preparation and Planning: Define the workshop’s objectives and identify key participants, including project team members, stakeholders, and other relevant experts.
- Initial Data Collection: Gather relevant information about the project and ask participants to reflect on what went well and what did not during the project.
Workshop:
- Identification of Lessons Learned: Explore successes and achievements, analyzing what contributed to these positive outcomes. Examine challenges and obstacles, identify underlying causes, and consider alternatives to address them in the future. Highlight opportunities for improvements in processes, communication, and risk management.
- Recording and Action Plan: Document the lessons learned using a standardized format and ensure the clarity and accuracy of the information. Develop a practical and tangible action plan to update standards and methodologies if necessary. Assign responsibilities, deadlines, and dates for the actions.
- Knowledge Sharing: Publicize the lessons learned document among the project stakeholders and relevant teams. Integrate the lessons learned into the organizational database of lessons learned.
Post-workshop:
- Follow-up on the Action Plan: Follow up on the action plan, verifying its correct implementation.
By following these steps, organizations can transform past experiences into strategic levers for future success, consolidating a proactive approach to continuous improvement in capital projects.
Structure of the Lessons Learned Record Form
A well-structured document is essential to ensure a systematic approach to capturing and applying lessons learned in projects. This form is a valuable tool for documenting experiences, insights, and recommendations that emerge throughout the project’s lifecycle.
- Project Details, Project Manager, and Dates:
Project: Identify the project with which the lesson learned is associated.
Project Manager: Name of the person managing and leading the project.
Dates: Record the project dates (start and completion) and the date the lesson was identified.
- Category of the Lesson Learned:
Classifying the lesson learned into specific categories, facilitating organization and later analysis. Examples include risk management, communication, and operational processes, among others.
- Description of the Lesson Learned:
Detail the specific problem, experience, or insight gained during the project with clear contextualization for comprehensive understanding, including relevant events, decisions made, and outcomes achieved.
- Impact:
Specify the lesson’s consequences or effects on the project and explore how the lesson influenced schedules, budget, quality, team dynamics, customer satisfaction, or other relevant aspects.
- Recommendations:
Propose actions/suggested changes for future projects based on the lesson learned and define corrective measures or preventive adjustments to be implemented.
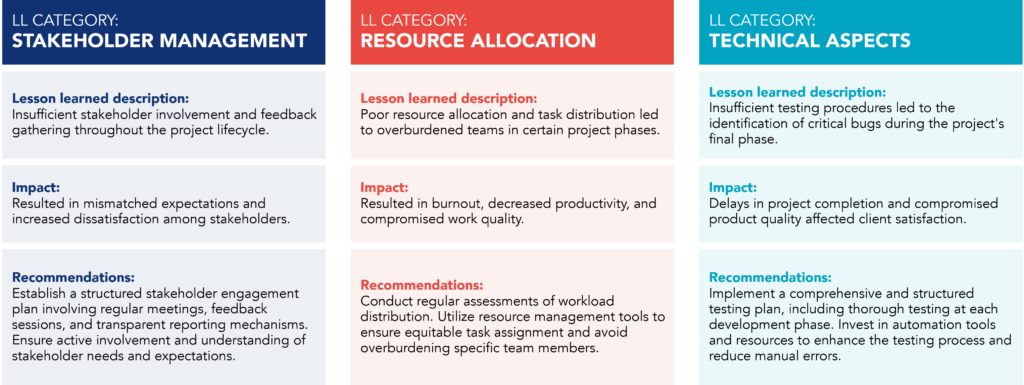
This form aims to ensure that each lesson learned is documented in a standardized and understandable manner, turning past experiences into actionable guidelines for the future. By systematically filling these fields, organizations create a valuable repository of knowledge that can be consulted and applied in subsequent projects, continuously strengthening operational effectiveness and organizational resilience.
Technology as a Support for Organizing and Sharing Lessons Learned
Technology can facilitate sharing lessons learned throughout the organization. The digital era offers innovative solutions for capturing, storing, and spreading valuable knowledge acquired from previous projects.
- Collaborative Platforms and Intranet: Implementing collaborative platforms and corporate intranets provides a centralized environment for storing lessons learned. It simplifies easy and quick access to relevant information by team members, promoting transparency and agility in the search for insights.
- Specific Databases: Develop specific databases for lessons learned, categorized by projects, thematic areas, or phases of the project lifecycle. This approach streamlines the search process, enabling teams to swiftly locate lessons that are pertinent to particular challenges or relevant subjects.
- Integration with Workflows: Integrating lessons learned platforms with existing workflows, incorporating the review of these lessons as a regular step in the project lifecycle. Ensures that the analysis of lessons learned is an embedded practice, promoting a culture of continuous learning.
When correctly applied, technology simplifies the management of lessons learned and transforms these insights into dynamic assets for the organization.
Conclusion
Capital projects require a strategic approach that goes beyond plain execution. Analyzing and applying lessons learned is essential to promote continuous improvement, share knowledge, improve risk management, and increase effectiveness and efficiency in future projects.
By recognizing that each project is a unique source of learning, organizations can correct past mistakes and actively shape the path to future success. Organizations forge a solid path to sustainable success in an ever-evolving business environment by adopting this continuous improvement mindset and being adaptable.
Still have questions about Lessons Learned?
What Are Examples of Lessons Learned in a Project?
Examples of lessons learned in a project can vary based on the nature of the project, its challenges, and the experiences gained. Some general examples include:
- Inadequate Risk Assessment: The initial risk assessment was not sufficiently thorough, leading to unexpected challenges. A more in-depth risk analysis will be conducted during the planning phase in future projects.
- Communication Failures: Poor communication among team members and stakeholders resulted in misunderstandings and delays. To address this issue, a communication plan with regular updates and transparent channels will be established for future projects.
- Resource Allocation Problems: Inadequate resource allocation led to project bottlenecks and delays. In the future, a more realistic resource estimation will be made, and contingency plans will be implemented.
- Insufficient Training: Team members faced challenges using new technologies or tools due to inadequate training. In future projects, a comprehensive training program will be implemented to ensure all team members are proficient in the required tools and technologies.
- Ineffective Project Monitoring: Inadequate project monitoring resulted in delays in meeting deadlines. A more robust planning and monitoring system will be implemented to ensure timely identification and resolution of issues.
These examples highlight the importance of reflecting on challenges and successes to extract valuable lessons that can increase the efficiency and effectiveness of future projects.
See more on Capital Project Excellence
Find out more about improving this business area
