If organizations want to reduce the risks associated with climate change, build a more just society, and generate growth, they must create more sustainable systems and economies.
A stronger ESG proposition can help ensure the long-term success of companies by turning them into change agents in the new sustainable economy. Companies that do not adopt ESG principles risk losing value in several ways.
What is ESG?
ESG is an acronym for Environmental, Social, and Governance and is the assessable outcome concerning a company’s overall sustainability performance.
Corporate sustainability creates long-term stakeholder value by implementing a strategy that addresses the needs of the environmental, social, and financial systems within which a business operates. The aim is to leave these systems capable of existing indefinitely.

Environmental Factors in ESG
Environmental sustainability refers to companies’ management of their direct and indirect ecological impacts, commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and climate change, and contribution to a decarbonized economy.
These are Environment main topics
- Carbon emissions
- Toxic emissions
- Energy efficiency
- Climate change vulnerability
- Water consumption and management of residual waters
- Biodiversity and land use
- Materials source
- Waste and hazardous substances management
- Product design and lifecycle management
- Green technology/green buildings/renewable energies
Social Factors in ESG
Social sustainability is linked to the management of people inside the organization and suppliers in promoting decent employment, policies of equal opportunities and balance between work and privacy, continuous training , and respect for human rights.
The main topics of social are:
- Workplace relations (inclusion and diversity)
- Health and safety
- Human capital development (training)
- Talent attraction and retention
- Work conditions in the supply chain
- Prevention and work safety
- Product safety and quality
- Data security and privacy
- Fair marketing and product labelling
- Community relations
Governance Factors in ESG
Governance sustainability integrates the commitment of companies to good governance, codes of ethics and conduct, transparency, and anti-corruption of the board, directors, and management team.
Governance main topics are:
- Board structure
- Employee Compensation
- Customer satisfaction
- Supply chain resilience
- Business ethics and transparency of payments
- Tackle corruption and instability
- Accountability for performance
- Systemic risk management
- Responsible/ impactful finance and investments
- Reporting and disclosure
What is the difference between ESG and CSR?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) are related but distinct, and it’s easy to conflate both. They’re different angles of measuring the company’s impact on sustainability.
While CSR is the internal initiative undertaken to achieve corporate sustainability purposes, ESG is guided by external requirements that reflect the external impact of the company’s sustainability strategy.
CSR gives a framework to sustainability agendas and business responsibility culture, while ESG is the action and measurable result. CSR can be considered the qualitative side, and ESG is the quantitative side of sustainability.
Why is ESG Important?
In recent years, organizations have re-evaluated the importance of ESG to their business. Sustainability is no longer considered a sideline area but a global framework that integrates the business’s strategic thinking.
Studies show that close to 3 in every 5 managers (57%) have already created a cross-functional ESG working group responsible for driving ESG strategy, and 42% are in the process of doing so.
It is increasingly clear that organizations that are integrating ESG into the strategy can have benefits for performance and sustainable business value. Intangible benefits such as increased stakeholder confidence and brand reputation, as well as more tangible and measurable benefits such as increased return on investment, reduced risk, and easier talent attraction and retention.
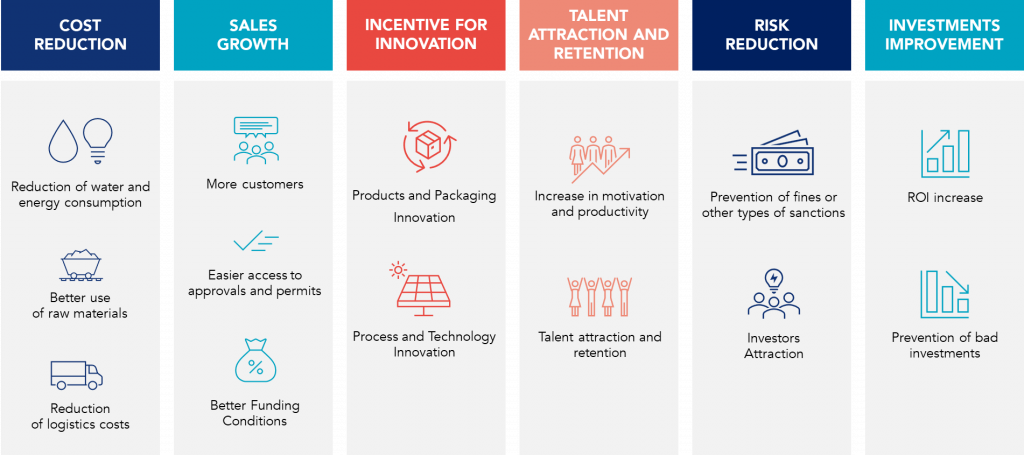
How ESG can help businesses
ESG factors have become key drivers of value, and ESG can help businesses in several ways:
- Cost Reduction
- Sales Growth
- Incentive for Innovation
- Talent attraction and retention
- Risk Reduction
- Investments Improvement
Cost Reduction
ESG strategies have a direct impact on cost reduction. They allow reducing operational expenses, such as raw materials, water, or electricity costs.
Studies prove that companies that carry out the most sustainable strategies are the ones that achieve the best resource efficiency and financial performance.
The reduction of costs can be achieved through different solutions, such as:
- Reduce water consumption;
- Reduce energy consumption and switch to renewable energy;
- Optimize raw material consumption, reducing waste;
- Produce recyclable or biodegradable products;
- Reduce and recycle the waste generated and form partnerships for its treatment;
- Improve logistics through route optimization.
Sales Growth
ESG attracts the preference of consumers. Customers are willing to pay to become “sustainable”. The commitment to sustainability is at the top of consumer trends for the coming years. The message is clear: there are increasingly ecologically, civically, and socially conscious consumers who buy the change they want to see in the world. Consumers want companies to think not only about their own growth but also about the quality of life of workers, consumers, and all the people involved in producing and developing their products and services.
Many banks and financial institutions offer companies with good ESG scores special terms. The reason is that these organizations are seen as less risky and more likely to pay their debts.
A strong ESG proposition also helps companies enter new markets and grow in those where they already do business. When government entities trust companies, they are more likely to have access to approvals and licenses that offer new growth opportunities.
Incentive for Innovation
ESG can be an essential driver of continuous improvement and innovation in organizations. Sustainability challenges companies to find more efficient products, packaging, processes, and technologies with less environmental impact.
The environmental criterion encourages companies to adopt more sustainable practices regarding using natural resources, emission reduction, and efficiency. This pressure to work more sustainably leads companies to seek to innovate their products and packaging to be more eco-friendly, with lower resource consumption, lower carbon footprint, and less waste generation. This may involve the development of biodegradable materials, recyclable packaging, and products with lower environmental impact throughout the life cycle, among other innovative solutions.
The same applies to the innovation of processes and technologies. Companies are encouraged to find cleaner technologies, and more efficient operations, that use renewable energy sources and allow the reuse of waste and water, among other innovative solutions.
All these innovations create competitive advantages that drive growth.
Talent attraction and retention
Having satisfied and engaged employees is one of the organizations’ most critical competitive advantages. A strong ESG strategy can help companies attract and retain talent and increase the overall productivity of the employees.
Research shows that happy employees are more productive. A sense of purpose can instill increased satisfaction. The greater an employee’s perception of the positive impact of their work, the greater their motivation.
Therefore, just as a greater sense of purpose can inspire employees to perform better, a weaker ESG proposition can increase dissatisfaction and reduce productivity. Two of the most striking examples of this are sick leaves and strikes.
Genuinely sustainable companies are better able to attract and retain employees who are looking for a company that provides them with a sense of purpose. This gains relevance to the younger generation. Modern employees do not want to work for companies whose practices harm society and the environment. In other words, with a solid ESG strategy, it is easier to attract the best candidates and keep them in the company.
Risk Reduction
Environmental and social issues began to play a more significant role in risk analysis and investment decisions.
ESG criteria can contribute to a holistic approach to risk management. As ESG incorporates standards for environmental management, working and safety conditions, respect for human rights, anti-bribery and anti-corruption actions, and compliance with relevant laws and regulations, companies ensure compliance by avoiding fines and other foreseen sanctions and ensuring the organization’s entire operation.
On the other hand, investors are also more interested in incorporating companies with strong ESG policies. Organizations that manage risk well are those most likely to attract the main investors. Recent studies show that 89% of investors in major global markets see ESG as a criterion to consider when evaluating an investment.
Investments Improvement
A consistent ESG strategy can positively impact the return on investments by applying capital to more favorable and sustainable opportunities.
Regarding sustainability issues, it is essential to be proactive because deciding not to act will often translate into a loss of money in the medium to long term. Maintaining high-energy consumption equipment or production processes with high raw material waste are examples of these decisions, in which doing nothing results in a cost to the company. Investments to upgrade equipment, facilities, or processes can be high, but postponing the decision can be even more costly.
Companies mindful of ESG criteria can identify opportunities and invest in more promising and sustainable resources (such as using renewable energy, adopting environmentally friendly processes, etc.). The same assessment helps organizations avoid investments that have a low return, have great potential to create environmental damage, and can contribute to the company’s poor reputation.
Why investors are increasingly interested in ESG
For all the above reasons, it is easy to understand why investors prefer companies with good ESG standards.
Companies with consistent ESG practices generally have a lower risk. The likelihood of facing legal problems, sanctions, or scandals because of environmental issues, non-compliance with labor laws, or corruption is lower.
In the last years, investors increasingly focus on companies with a favorable ESG impact. This means that companies must show a genuine commitment to sustainability to attract and maintain investors’ capital.
What is ESG Investing?
ESG Investing means making investments prioritizing optimal environmental, social, and governance factors and outcomes. ESG investing is a way of investing “sustainably”, where investments are made respecting the environment, people and society, and economy.
Below is a diagram prepared by the OECD (Organisation de Coopération et de Développement Économiques). In the first line, there is a definition of the types of investments, and in the lines below, an explanation of what is expected of each type of investment.
Conventional financial investment is the traditional investment, best known in the market, where environmental, social, and governance issues are not considered. The focus of these investments is only to generate competitive financial returns.
At the opposite extreme is the philanthropy investment, which is not intended to generate any return for investors. The focus is to create some social or environmental impact.
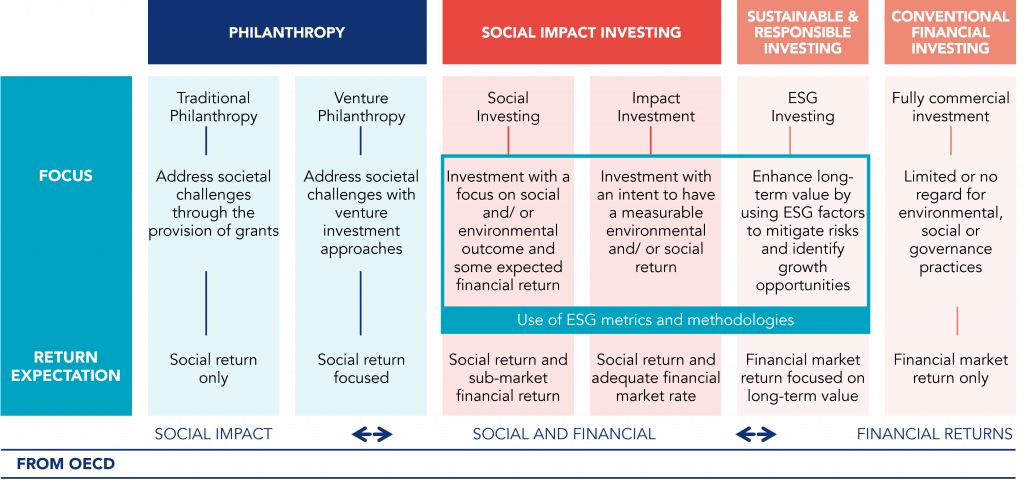
ESG investing needs to have a social or environmental impact and a financial hit, meaning they need to generate value. These investments are aimed at developing results for investors in the short, medium, or long term while generating “ESG impact”.
The Future of ESG
The sustainability field is expected to evolve in an accelerated manner over the next decade. From new laws and regulations to sharper consumer and employee demands, as well as investor expectations.
ESG reporting has received considerable attention in the past few years, contributing to a ‘boom’ in sustainability reporting standards, goals, and regulations.
Now, many organizations are claiming that sustainable practices are a strategic ambition. However, sustainability has had a parallel agenda and is still managed as a stand-alone initiative, resulting in disorganized execution and slow progress.
Companies must choose a sustainable business strategy rather than a sustainability strategy. ESG should be fully integrated into corporate strategy and not be subordinated to other strategies.
Here are the 4 steps to integrate sustainability into your organization’s strategy:
- Review and plan the business strategy: Companies need to define an ESG strategy supported by a conviction, distinctive and meaningful to their stakeholders, that resonates with the market, and that is aligned with their purpose.
- Deploy the strategy until the point of impact: Without action plans, there is no strategy. At the point of impact, the strategy materializes with objective guidelines of ‘what’, ‘when’, ‘how’ and ‘how much’ we want to achieve.
- Implement the strategic breakthrough initiatives: Following a structured approach is critical to ensure breakthrough improvements’ success, maximize outcomes, and ensure they are perpetuated.
- Monitor results and implement countermeasures: Sustainability reports should mirror the ongoing effort to pursue priorities and achieve strategic goals.
To improve corporate sustainability in the future, companies need to move from ignorance to competitive advantage.
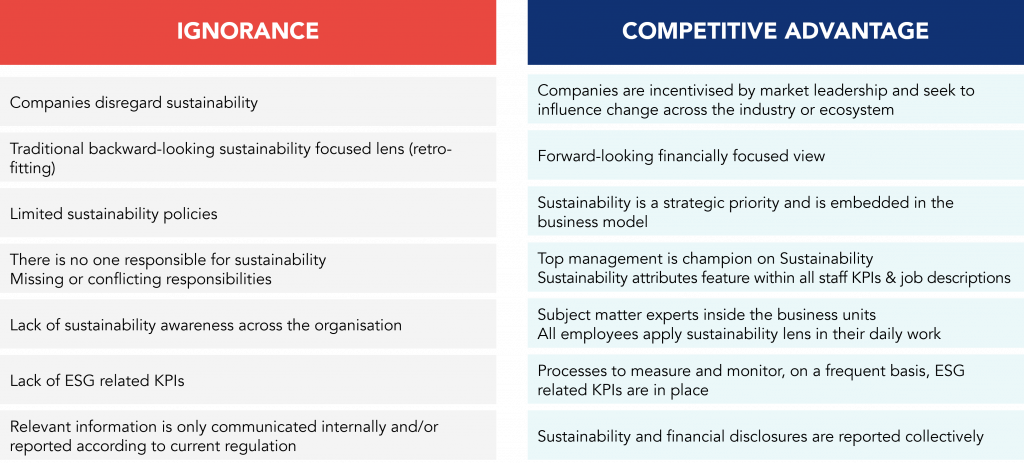
For companies, the planet, and society to have a promising future, companies must develop a sustainable business strategy that consistently works on the three ESG factors.
Still have some questions about ESG?
How can ESG metrics influence investment decisions in emerging markets?
ESG metrics play a crucial role in shaping investment decisions in emerging markets by offering a more comprehensive understanding of risks and opportunities associated with sustainability practices. Investors increasingly consider ESG factors as indicative of effective management practices and lower risk profiles. In emerging markets, where regulatory frameworks may be less robust, strong ESG scores can signal operational excellence and resilience, attracting investment by reducing perceived risks.
What technologies are transforming ESG data collection and reporting?
Advancements in technology have significantly improved ESG data collection and reporting. Key technologies include artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, which enhance the analysis of large data sets, providing more accurate and granular ESG insights. Also, blockchain technology is increasingly used for its capability to offer transparency and traceability in supply chains, crucial for verifying sustainable practices. Additionally, Internet of Things (IoT) devices help monitor and manage resource use and emissions in real-time, making data more reliable and actionable for companies aiming to improve their sustainability performance.
What are the latest developments in global ESG regulation?
Global ESG regulations are rapidly evolving, reflecting the growing importance of sustainability issues on the international agenda. Recent developments include the European Union’s Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR), which aims to increase transparency in how financial market participants consider sustainability risks in their investment decisions. Similarly, the US Securities and Exchange Commission is considering rules that would require public companies to disclose more information on climate risks and greenhouse gas emissions. These regulations are designed to standardize ESG disclosures, making it easier for investors to compare and assess companies’ sustainability credentials across borders.
See more on Sustainability
Find out more about improving this business area
