In today’s landscape, the global markets’ dynamism and the increasing consumer expectations – seeking fast deliveries and reduced costs – place unprecedented pressure on warehousing and distribution operations. In an increasingly connected world, where sustainability is a priority and technology advances by leaps and bounds, companies of all sizes seek ways to enhance their supply chains’ efficiency to stay competitive. This scenario demands optimizing existing processes, continuously innovating, and adopting sustainable practices to meet current needs without compromising future generations.
Understanding the Dual Role of Warehousing and Distribution in Supply Chains
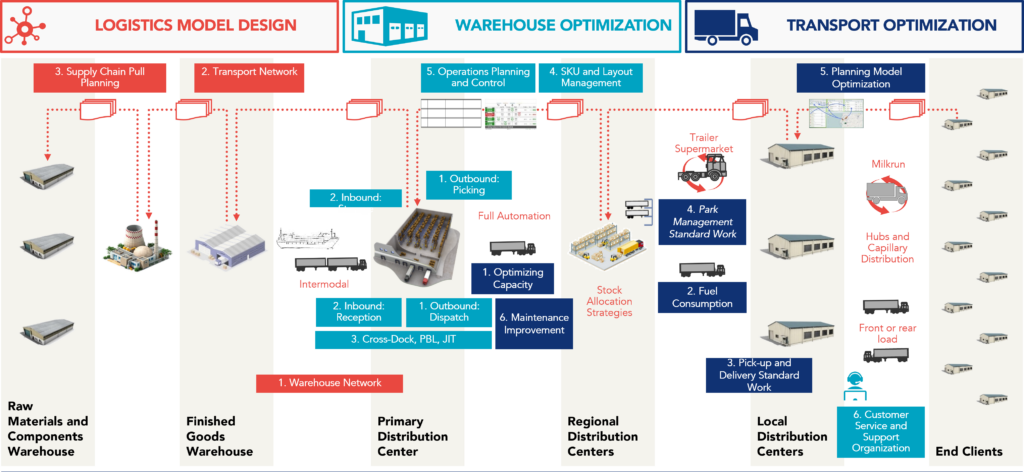
Warehousing and distribution are essential elements in supply chains, acting as fundamental links between production and consumption, which are crucial for good customer service and cost management.
Warehouses are more than just storage spaces; they also encompass reception, storage, order preparation, shipping, cross-docking, customer service, and operational planning and control. They take a strategic position in the dynamics of product flow, inventory optimization, cost reduction, and logistics efficiency maximization.
Distribution, in turn, is the link ensuring the delivery of products to consumers or points of sale, incorporating logistics planning, pickup and delivery, load capacity optimization, and vehicle maintenance. An efficient distribution strategy ensures the right products reach the right place at the right time and conditions.
Effective integration between warehousing and distribution is essential for optimizing supply chains. Synchronizing these activities allows for a quicker response to demand changes, reduces stock excess, improves storage space utilization, and increases transportation efficiency. An excellent logistics model optimizes warehouses’ network and operation (warehouse location and stock allocation) and transportation (transportation categories and distribution strategies).
Core Principles for Effective Warehousing
Effective warehousing is essential in modern supply chains, ensuring products are kept in optimal conditions and available for distribution at the right time. This chapter addresses the Lean principles that underpin effective warehousing.
Warehouse Layout and Picking
Efficient warehouse design and optimized picking practices are essential to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in any supply chain.
Let’s explore the principles of warehouse design:
- Organization by Value Stream: Grouping items based on product family, market/customer, similar picking methods, or similar storage specifications helps in quickly locating items and reducing order preparation time.
- Flow-Oriented Layout: Adopting a U-shaped layout with coinciding or close entry and exit areas promotes a continuous workflow and minimizes wasting time in unnecessary movements.
- Location by Consumption: Positioning products according to consumption frequency significantly reduces distances traveled during picking and storing operations, optimizing operator time.
- Packaging Units and Storage Areas Optimization: Adjusting packaging units and configuring storage areas to accommodate products efficiently can significantly improve space utilization.
- Visual Management and Standardization: Implementing visual signals and standardizing processes can help quickly identify items and consistently execute operations, reducing errors.
- Daily Operations Management: Real-time productivity, quality, and monitoring of other KPIs allows for early problem detection and swift corrective decision-making.
- Safety, Ergonomics, and Error-Proofing Systems: Designing the warehouse with a focus on safety and ergonomics minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries while error-proofing systems (poka-yoke) help prevent operational errors.
Another essential practice in a warehouse is having a good picking process, as this is a significant portion of direct warehouse labor costs. Next, we will address some of the good practices in picking:
- Separate Picking and Replenishment: Dedicating exclusive aisles for picking and replenishment reduces interference between these activities, increasing efficiency and safety.
- Dimensions Adapted to Product and Consumption: Keeping the dimensions of aisles and picking positions to a minimum reduces distances and improves productivity.
- Adjust Picking Strategies: Defining picking strategies – batch picking, multi-order, pick and pack, picking by line, picking by store, cross-docking – according to order profiles can significantly increase productivity.
- Make “A” References Accessible: Positioning the most sought-after items (“A” references) in easily accessible locations maximizes picking efficiency.
- Frequently Ordered Items Located Close to Each Other: Placing items commonly ordered together in close positions can reduce picking time.
- Eliminate Unnecessary Records and Documents: Streamlining processes by eliminating redundant documentation speeds up operations and reduces errors.
- Hands-Free Picking: Implementing solutions that allow hands-free picking, such as headsets for vocal instructions (voice picking) increases productivity.
Leveraging Infrastructure and Technology
The success of a warehousing system largely depends on its infrastructure and technology integration. The physical infrastructure, such as warehouse construction, shelving systems, and material handling equipment, should be designed to maximize space use, facilitate access to products, and ensure stored items and workers’ safety.
On the other hand, technology plays a crucial role in optimizing warehousing operations. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are essential for efficient inventory organization, allowing for an accurate view of stocks, optimizing order preparation, and minimizing errors. Other technologies, such as automation through storage and replenishment robots, radiofrequency identification (RFID) systems, and solutions based on artificial intelligence, can significantly increase efficiency while simultaneously reducing operational costs.
Data integration and advanced analysis also allow for more accurate demand forecasts and better inventory management, ensuring that resources are used as effectively as possible.
The Art of Selecting the Best Warehouse Location
Choosing warehouse locations is a strategic decision that can significantly impact the supply chain’s efficiency and costs. This choice and the number of warehouses needed should consider the target service level. An ideal location balances closeness to suppliers, customers, transportation networks, and operational and land costs.
Some critical factors in choosing a warehouse location:
- Close to the target market;
- Easy access to transport infrastructures (highways, ports, and airports);
- Skilled labor availability;
- Economic considerations (land costs, tax incentives, and operational costs);
- Prospects for future expansion.
Analytical frameworks like market analysis, transportation cost evaluation, and scenario simulations can help make informed decisions. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools are often used to visualize demographic, economic, and transportation data, helping to identify ideal locations.
Selecting a warehouse location requires carefully analyzing multiple factors to find the balance that meets the supply chain specific needs.
Distribution: The Vital Link in Supply Chain Excellence
Distribution is a critical component in the supply chain, acting as the link between production and consumers. This section explores how creating integrated distribution mechanisms and effective risk management are vital in ensuring operational excellence and customer satisfaction.
Crafting Integrated Distribution Structures for Peak Performance
Efficient distribution requires integrating various functions and processes to ensure products are delivered to customers efficiently. Creating integrated distribution processes involves coordinating suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, and carriers, using technology to synchronize and optimize operations.
Technology plays a key part in an integrated distribution system. Transportation Management Systems (TMS), e-commerce platforms, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Track and Trace systems, and advanced analytics tools enable coordination and real-time order tracking. These technologies facilitate communication among all parties involved in the supply chain, allowing for faster and more informed decisions.
Effective distribution strategies can significantly reduce delivery times and costs, such as cross-docking, direct-to-consumer (DTC) distribution, and strategically located distribution centers. Choosing the right distribution strategy depends on meticulously analyzing the market, products, and customer expectations.
Ensuring Distribution Reliability through Risk Management
Reliability in distribution is essential for maintaining customer trust and brand integrity. Risk management is crucial in identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to supply chain efficiency.
The first step in risk management is identifying and assessing potential risks that could affect distribution operations. This includes risks associated with transportation delays, product damage, technological failures, and supply chain disruptions due to natural disasters or political instabilities.
Once risks are identified, developing and implementing mitigation strategies is crucial. This can include diversifying transportation routes and suppliers, investing in insurance, implementing backup technological systems, and creating contingency plans.
Real-time monitoring tools and early warning systems can help companies quickly identify problems and implement corrective actions before risks materialize into significant disruptions.
Pursuing Operational Excellence in Warehousing and Distribution
The pressure on warehousing and distribution operations has significantly increased due to growing consumer expectations for fast deliveries, reduced costs, and a significant increase in supply chain complexity. Operational excellence in warehousing and distribution is vital for companies to remain competitive in increasingly demanding markets. This section highlights the importance of continuous improvement and how it can raise warehousing and distribution teams to a high-performance level, ensuring processes are efficient, resilient, and adaptable to market changes.
Applying Continuous Improvement for High-Performance Warehousing and Distribution Teams
A continuous improvement culture in the context of warehousing and transportation means establishing an organizational environment where improvement, innovation, and excellence in warehousing and distribution operations are a common priority across all levels of the organization. There is always room to optimize processes, increase value chain efficiency, and improve customer service quality in this environment.
Integrating continuous improvement into daily activities encourages employees to look at data and question how processes can be more agile, safe, and efficient. Adopting an improvement culture in warehousing and transportation brings significant benefits, such as improved warehouse inventory management, increased productivity in storage, picking, and shipping activities, higher transportation utilization rates, better capacity planning, optimized delivery routes, reduced fuel consumption, and increased speed and quality in order fulfillment. Additionally, it makes the organization more agile and resilient, ensuring its long-term competitiveness.
Future Trends and Innovations in Warehousing and Distribution
As we advance into the 21st century, the warehousing and distribution sector faces significant changes driven by technology, consumer expectations, and the growing need for sustainable practices. The following part explore one of the emerging trends: incorporating green practices in warehouse and distribution.
Sustainability and Green Practices in Modern Warehouse and Distribution
As global environmental awareness grows, sustainability and green practices become increasingly vital in distribution. These practices contribute to preserve the environment and offer competitive advantages, such as cost reduction and improved brand image.
- Sustainable Construction and Design: Adopting green building standards, such as Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED), is becoming more common in new and renovated warehouses. This includes using sustainable materials, energy-efficient systems, green roofs, and maximizing natural light.
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Sources: Warehouses are also implementing advanced energy management systems, including LED lighting, high-efficiency heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, and installing solar panels. These measures not only reduce the carbon footprint but also operational costs.
- Low-Emission Vehicles: One of the most significant changes in sustainable distribution is the transition to low-emission vehicles. Organizations are investing in electric, hybrid, or alternative fuel-powered vehicles, such as biogas, for deliveries. This shift reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
- Route Optimization: Advanced route management software allows companies to optimize deliveries, reducing the distance traveled and, therefore, fuel consumption. These tools analyze customer time windows, traffic, distances, and load capacity to set the most efficient routes. Route optimization improves fuel efficiency, maximizes fleet utilization, and reduces delivery time.
- Eco-Friendly Packaging: Using eco-friendly packaging is another sustainable element. This includes reducing packaging material, using recycled or biodegradable materials, and implementing packaging return schemes. These initiatives reduce waste and contamination and encourage a circular economy where materials are used for as long as possible.
Conclusion: Integrating Warehousing and Distribution for Competitive Advantage
As the global business landscape evolves, effectively integrating warehousing and distribution is a critical strategy for companies seeking a sustainable competitive advantage.
The ability of organizations to adapt to market changes, consumer expectations, and environmental pressures is not just a necessity; it’s an opportunity to achieve differentiation. Companies that can balance warehousing and distribution operations with efficiency, sustainability, and innovation are well-positioned to thrive.
The foundations for competitive advantage are:
- Improvement Culture: A continuous improvement and innovation culture ensures that teams remain competitive, focused on waste elimination and value creation, and aligned with industry best practices.
- Technology and Innovation: Adopting advanced technologies, such as automation, artificial intelligence, and data analysis, allows to optimize processes, better manage inventory, and increase distribution efficiency.
- Sustainability: Incorporating sustainable practices reduces environmental impact and responds to the growing consumer demand for corporate responsibility, potentially generating operational savings.
- Flexibility and Agility: Implementing integrated management systems provides the flexibility to respond quickly to market changes and customer needs.
The future of warehousing and distribution will be defined by the ability to integrate these elements together, leveraging data and new technologies to create logistics systems that are efficient, resilient but also adaptable and sustainable. Companies prioritizing this integration will be better equipped to face future challenges, from demand fluctuations to global sustainability issues.
Still have some questions about Warehousing and Distribution?
What are advanced warehouse management systems (WMS)?
Advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) are software designed to optimize warehousing operations, facilitate inventory management, improve picking and packing accuracy, reduce operational costs, and increase overall warehouse efficiency through automation and real-time data collection.
What is the importance of warehouse safety?
Warehouse safety is crucial to protect employees from accidents, minimize damage risks to stored products, and ensure compliance with legal regulations. A robust approach to safety can also improve operational efficiency and the company’s reputation.
What is the difference between warehousing and distribution?
Warehousing refers to holding products in a location until they are needed, involving stock management and optimizing space and storage operations. On the other hand, distribution deals with delivering products to consumers or points of sale, involving transportation, route management, and logistics.
What are the benefits of integrating sustainability in warehousing?
Integrating sustainability in warehousing can reduce operational costs (for example, through energy savings), minimize environmental impact, improve brand image and customer satisfaction, encourage innovation, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
See more on Logistics
Find out more about transformation in this sector
See more on Warehousing & Distribution
Find out more about improving this business area
