In the current landscape, increasing profits and enhancing environmental impact aren’t conflicting goals; they’re actually intertwined strategy pillars. The growing global awareness of environmental effects and an increasing concern for social responsibility have transformed how companies operate.
In this article, we explore the importance of a Corporate Sustainability Strategy that goes beyond the traditional limitations of profit and considers social and environmental impacts in decision-making. We will see how integrating sustainable business models and adopting ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) criteria redefine the modern business landscape. Finally, we will analyze the need to align short-term objectives with long-term sustainability goals and envision a future where business models embed sustainability as a core part of the company’s identity.
This article presents the inherent advantages of adopting a corporate sustainability strategy for companies’ finances and the planet’s health.
What is a Sustainability Strategy
A sustainability strategy is a comprehensive and goal-oriented plan an organization develops to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into its operations, decision-making, and corporate culture. The main objective of this strategy is to align the company’s practices and goals with sustainability principles.
A sustainability strategy goes beyond isolated actions or specific social or environmental responsibility initiatives. It integrates sustainability principles into the core business processes, aiming to create long-term value for the company and society. This involves considering how the company’s activities affect issues such as climate change, natural resource use, human rights, diversity and inclusion, business ethics, and transparency.
A successful sustainability strategy mitigates risks, creates opportunities for innovation, growth, talent attraction, and retention, and improves reputation and brand value. To ensure its effectiveness, sustainability must be embedded in the company’s culture, from top management to every operational level.
Why is a Sustainability Strategy important?
A sustainability strategy is essential for companies for several reasons, transcending environmental and social benefits. By considering ESG factors (Environmental, Social, and Governance) and implementing a sustainable strategy, companies can reap significant advantages at various levels:
Cost Reduction:
ESG strategies directly reduce costs by promoting resource efficiency. By implementing sustainable practices, such as reducing water and energy consumption, optimizing raw materials use, and improving logistics, companies can decrease operational expenses and enhance their financial performance.
Sales Growth:
ESG factors influence consumer preferences. Many customers prefer sustainable products and services, which can lead to an increase in sales. Additionally, companies with good ESG scores often receive favorable conditions from financial institutions, as they are seen as having lower risk.
Promoting Innovation:
Sustainability can drive innovation within organizations. The need to operate sustainably encourages companies to seek innovative solutions with a lower environmental impact, such as developing recyclable materials, reducing waste, and adopting cleaner technologies.
Talent Acquisition and Retention:
An ESG strategy can help companies attract and retain qualified talent. Employees, especially from the younger generation, seek jobs with a purpose and are drawn to companies that care about sustainability. A strong ESG value proposition can increase job satisfaction and productivity.
Risk Reduction:
ESG offers a comprehensive approach to risk management. By incorporating standards related to environmental management, worker safety, human rights, and compliance with laws and regulations, companies can mitigate risks associated with fines, legal actions, and reputation damage. Investors also see strong ESG policies as indicators of effective risk management.
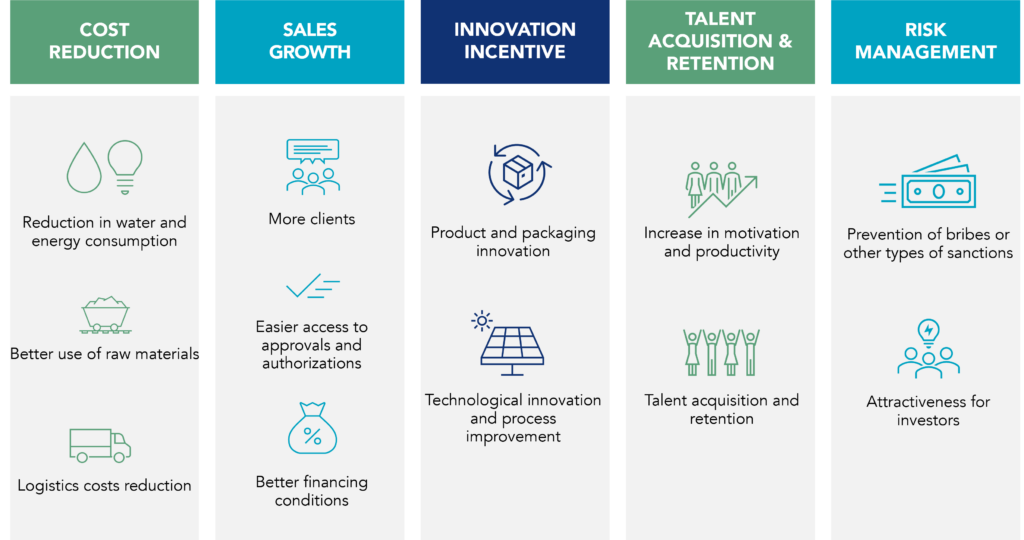
A sustainability strategy contributes to the planet’s health and communities. It offers tangible gains in efficiency, business growth, innovation, talent attraction, risk reduction, and financial performance. This approach aligns with modern values and drives sustainable long-term business success.
Building a Robust Sustainability Strategy with Sustainable Business Models
Building a robust sustainability strategy with sustainable business models is imperative for all companies today. Integrating sustainability into the core of the business strategy is essential not only to meet stakeholder expectations but also to ensure long-term resilience and create lasting value.
Defining and Explaining a Sustainable Business Model
A sustainable business model is a strategic approach adopted by companies seeking to balance their financial objectives with a positive impact on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) dimensions. Unlike traditional business models, which may prioritize profit exclusively, an efficient and sustainable business model includes broader considerations to ensure the company contributes responsibly to society and the environment.
This model aims to create economic, social, and environmental value beyond short-term financial return maximization. This involves, for example, integrating energy efficiency practices, responsible use of natural resources, promoting diversity and inclusion, respecting human rights, and transparency in operations.
Key Elements of a Sustainability Strategy
A sustainability strategy encompasses several essential elements that guide the company’s actions toward more responsible and sustainable practices. Some of the key features are:
Top Management Commitment
The involvement and commitment of the organization’s leadership are fundamental to the success of the sustainability strategy.
Impact Analysis
It is essential to comprehensively analyze the environmental, social, and economic impacts of the organization’s operations to identify improvement areas.
Clear Objectives
To guide progress, define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) sustainability goals and objectives.
Standards and Procedures
Develop standards and procedures that address ESG issues and ensure they are communicated and implemented throughout the organization.
Stakeholder Engagement
Identify and engage key stakeholders such as employees, customers, suppliers, local communities, and shareholders to gain support and feedback regarding the sustainability strategy.
Risk and Opportunity Assessment
Assess the risks and opportunities related to sustainability that can affect the organization and develop plans to mitigate risks and seize opportunities.
Reporting and Transparency
Transparently communicate progress and challenges related to sustainability through periodic reports.
Sustainable Innovation
Encourage research and development of more sustainable products and processes that reduce environmental impact.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Comply with all industry or region-related sustainability laws and regulations.
Performance Evaluation and Continuous Improvement
Regularly measure performance against established sustainability goals and review the improvement strategy.
Education and Training
Get training in sustainability issues to promote adopting more sustainable practices in the workplace.
External Collaboration
Collaborate with other organizations, governments, NGOs, and civil society initiatives to address global sustainability challenges.
Developing a Sustainability Strategy
Companies must choose a sustainable business strategy that is more than a sustainability strategy. Sustainability should be fully integrated into the organization’s strategy.
Developing a sustainable strategy requires a well-structured process:
Review and plan the business strategy
The starting point is defining an fundamentally sustainable business strategy. This strategy must be anchored in solid convictions, be distinctive, relevant to stakeholders, aligned with the market, and reflect the company’s purpose.
Deploy the strategy up to the point of impact
Without an action plan, there is no strategy. At the point of impact, the strategy materializes with clear indications of ‘what’, ‘when’, ‘how’, and ‘how much’ we want to achieve. This involves formulating sustainability goals that should be publicly communicated.
Implement disruptive strategic initiatives
Following a structured approach is crucial to ensure the success of groundbreaking improvements, maximize results, and sustain them. An ESG improvement framework can be instrumental in implementing major projects, such as reducing transport emissions, increasing energy efficiency, or improving employee motivation.
Monitor results and implement countermeasures
Sustainability reports must accurately reflect the ongoing effort to pursue established priorities and achieve strategic objectives. Monitoring progress is vital to assess the impact of actions and identify areas needing adjustments. When results do not meet expectations, effective countermeasures need to be implemented to ensure the strategy remains on the right course.
By following these steps, companies can create a solid foundation for a comprehensive and effective sustainable strategy that brings financial benefits and positively impacts the environment and society.
When defining, deploying, and implementing the strategy, using KAIZEN™ methodologies and Lean principles can be beneficial, as these approaches not only facilitate results but also ensure their quality.
The 3 Pillars of Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability is founded on the three essential pillars of ESG:
- Environment: Addresses responsible management of natural resources, environmental impact reduction, energy efficiency, water conservation, sustainable materials use, and mitigation of climate change.
- Social: Involves promoting diversity and inclusion, respect for human rights, improvement of working conditions, respect for local communities, and responsibility towards stakeholders.
- Governance: Focuses on transparency, ethics in business, accountability, solid governance practices, and ensuring that decisions are aligned with the interests of all stakeholders.

By integrating these three foundations, companies can build a holistic approach to sustainability, aligning their financial goals with broader responsibilities toward society and the environment.
How ESG and Sustainability Strategy Meet in the Modern Business Landscape
The concepts of ESG and Sustainability Strategy are closely linked, working together to drive corporate success responsibly and sustainably. ESG represents the measurable outcomes related to a company’s overall sustainability performance.
In the modern business landscape, ESG plays an increasingly important role. The field of sustainability is expected to undergo rapid evolution over the next decade due to various significant factors, including new laws and regulations, heightened demands from consumers and employees, and growing expectations from investors.
New laws and regulations drive accountability and the adoption of more transparent and ethical practices. The growing awareness among consumers and employees about environmental and social issues leads companies to actively consider their impact and adopt measures to address legitimate concerns.
Furthermore, investors increasingly recognize ESG’s importance as an indicator of future performance. They view a company’s commitment to ESG issues as critical in assessing investment risks and opportunities.
These changes create an environment where ESG is no longer an option but a strategic need. Companies are pushed to adopt more holistic and sustainable approaches that consider economic, social, and environmental impacts in their decisions and actions.
Aligning Short-term Goals with Long-term Sustainability
Aligning short-term objectives with long-term sustainability is a fundamental principle to ensure that actions and decisions made in the present do not compromise an organization’s viability and future success. This alignment is crucial to a sustainable business strategy and significantly impacts a company’s financial, social, and environmental performance. Some ways companies can achieve this alignment include:
Integrating Sustainability Goals (ESG) into Short and Long-Term Targets:
When setting short-term goals aligned with long-term objectives, it is essential to incorporate sustainability considerations. This means establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect financial goals and progress on environmental and social metrics.
Holistic Planning and Strategic Priorities:
Companies should adopt a holistic approach to planning, considering the impacts of current decisions on future operations. This involves evaluating how short-term actions can influence the company’s reputation, environmental risks, and long-term customer and employee satisfaction. Short-term goals should be prioritized based on their impact on long-term sustainability.
Incentives and Recognition:
To foster alignment, companies can link incentives and rewards to short-term sustainable outcomes that contribute to long-term objectives. This demonstrates the company’s commitment to sustainability and motivates employees to act responsibly.
Transparent Communication
It is essential to communicate internally and externally how short-term objectives contribute to the long-term vision of sustainability. Transparency reinforces the company’s commitment and builds trust among stakeholders.
Continuous Monitoring:
Regularly tracking progress against short-term goals is crucial to ensure the company is on the right path toward long-term sustainability.
Aligning short-term objectives with long-term sustainability strengthens the company’s resilience and positions it to face emerging challenges and capitalize on future opportunities. This demonstrates a commitment to corporate responsibility and building a lasting legacy.
The Future of Sustainable Business Models
The future of sustainable business models is promising and becoming increasingly instrumental to business success. As awareness of ESG challenges grows, companies adopt more responsible and sustainable approaches to operation. Here are some trends indicating the direction sustainable business models may take in the future:
Total Sustainability Integration
Sustainable business models will no longer be seen as add-ons but as an intrinsic part of operations. Sustainability will be embedded in all business decisions and practices, from the supply chain to organizational culture.
Circular Economy
Businesses are adopting circular approaches, designing products and processes to minimize waste and maximize resource reuse.
Sustainable Innovation
The requirement for innovations that meet market needs while reducing environmental impact will be a priority.
Digitalization and Technology
Technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics will optimize processes, monitor environmental performance, and improve operational efficiency, resulting in more sustainable practices.
Transparency and Traceability
Consumers and investors will demand greater transparency regarding companies’ sustainability practices. Tracking technologies will allow stakeholders to know products’ traceability and lifecycle.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Addressing global challenges requires inter-industry collaboration and partnerships with governmental and non-governmental organizations. This may result in joint efforts to address climate change and social inequality.
Sustainable Investments
The growing demand for socially responsible investments will lead companies to demonstrate their commitment to sustainability to attract conscientious investors.
Local Development and Sustainable Communities
Companies will focus more and more on contributing to developing their communities, ensuring that their activities benefit local people and the environment.
Stricter Regulations
Governmental regulations on sustainability are likely to increase, pressing companies to adopt more responsible practices.
The future of sustainable business models involves a profound transformation in how companies operate, viewing sustainability not as an option but as a requirement. As these trends set, companies adopting sustainable business models will be better prepared to face emerging challenges, attract stakeholders, and thrive in an increasingly conscious and responsible world.
Still have some questions about Sustainability Strategy?
What is Corporate Sustainability?
Corporate sustainability, often called corporate social responsibility (CSR) or corporate responsibility, refers to the approach companies take to balance their economic objectives with social and environmental concerns.
What is ESG?
ESG is an acronym that stands for three critical factors used to evaluate and measure a company or organization’s environmental, social, and governance performance. ESG is used as a set of criteria to assess a company’s overall performance concerning sustainability and corporate responsibility issues.
What is an ESG framework?
An ESG framework is a structure or set of guidelines that companies use to assess and report performance in environmental, social, and governance matters. These metrics measure the impact of a company’s activities on ecological sustainability, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices. Investors, regulators, and other stakeholders are increasingly interested in assessing companies’ performance in these areas, leading to the development of ESG frameworks. Some of the most well-known and used include:
- Global Reporting Initiative (GRI): This is one of the world’s most widely adopted sustainability reporting frameworks. It provides detailed guidelines for companies to report their performance on sustainability issues, covering a broad range of ESG topics.
- Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB): The SASB develops industry-specific standards, helping companies to identify and report on the ESG indicators most relevant to their industry.
- Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD): This framework focuses specifically on disclosing information related to climate change and its financial impacts on companies.
Choosing an ESG framework depends on the company’s industry, objectives, and priorities. These frameworks help organizations measure and communicate their ESG performance consistently and transparently, which is increasingly essential for attracting investors, meeting customer expectations, and complying with sustainability-related regulations.
See more on Sustainability
Find out more about improving this business area
